Structure of the plant plastid-encoded RNA polymerase
Abstract
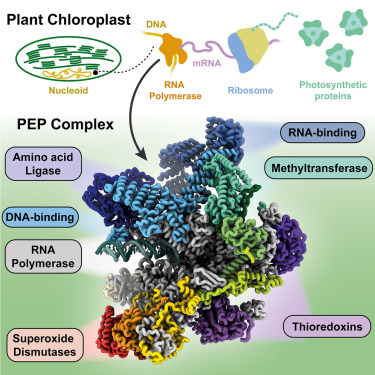
엽록체 유전자는 광합성과 관련된 단백질을 코딩하며 주로 *Plastid-encoded RNA polymerase(PEP)에 의해 전사된다. PEP은 박테리아 RNA polymerase (RNAPs)와 유사한 Plastid-encoded 단위체들로 구성된 다중-단위체 복합체로, nucleus에서 encoded된 PEP-연관 단백질(PAPs) 세트에 안정적으로 결합한다. PAPs는 PEP 활동과 엽록체의 biogenesis에 필수적이지만, 그 역할은 잘 정의되어 있지 않다. 여기서, 우리는 백색 겨자(Sinapis alba)로부터 native 21-subunit PEP와 PEP 전사 elongation 복합체의 cryoelectron microscopy (cryo-EM) 구조를 제시한다. 우리는 PAPs가 핵심 polymerase를 둘러싸고, 복합체 조립과 안정성을 증진시키는 것으로 보이는 광범위한 상호작용을 형성한다는 것을 확인했다. 연장 과정에서, PAPs는 transcription bubble의 downstream DNA 및 신생 mRNA와 상호작용한다. 이 모델들은 PEP의 subunit인 superoxide dismutase, lysine methyltransferase, thioredoxin, 그리고 amino acid ligase 효소의 세부사항을 밝혀낸다. 종합적으로, 이 데이터는 엽록체 전사와 식물 성장 및 적응에 있어서의 그 역할에 대한 기계적 이해의 기반을 제공한다.
* Plastid: 식물 세포와 조류 세포에 있는 세포소기관의 한 유형으로, 엽록체를 포함.
** Transcription bubble: RNA polymerase가 DNA를 전사하는 동안 DNA 이중나선이 분리되어 RNA 합성이 일어나는 영역.