GSDMB pore formation의 구조적 기반과 IpaH7.8에 의한 표적화.
Abstract
Gasdermins (GSDM)은 pore를 형성하는 단백질로, pyroptosis를 통해 host defence에 중요한 역할을 합니다. GSDM 중에서도 GSDMB는 lipid-binding profile이 뚜렷하고 pyroptotic potential에 대한 합의가 부족하기 때문에 독특합니다.
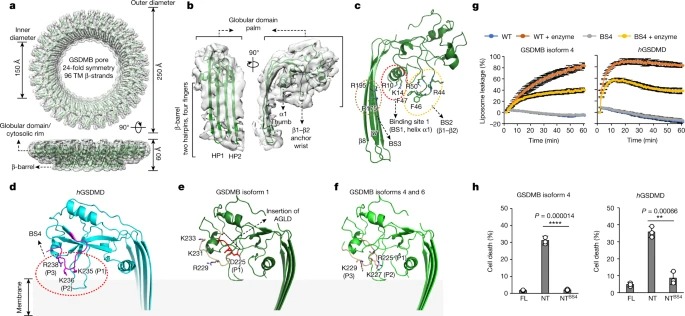
최근 GSDMB는 pore-forming activity를 통해 직접적인 bactericidal activity를 나타내는 것으로 나타났습니다. Intracellular human-adapted enteropathogen인 Shigella는 GSDMB의 ubiquitination-dependent proteasomal degradation를 유발하는 virulence effector인 IpaH7.8을 분비하여 이러한 GSDMB-mediated host defence를 회피합니다. 여기에서는 Shigella IpaH7.8 및 GSDMB pore와 복합된 인간 GSDMB의 cryogenic electron microscopy structure를 보고합니다. GSDMB-IpaH7.8 complex의 구조는 IpaH7.8에 의해 인식되는 구조 결정 인자로서 GSDMB의 세 개의 음전하를 띤 잔기의 모티프를 확인합니다. 쥐가 아닌 인간 GSDMD에는 이 보존된 모티프가 포함되어 있어 IpaH7.8의 종 특이성을 설명합니다. GSDMB pore structure는 GSDMB의 alternative splicing-regulated interdomain linker가 GSDMB pore formation의 regulator로서 작용하는 것을 보여줍니다. canonical interdomain linker를 가진 GSDMB isoforms은 정상적인 pyroptotic activity를 보이는 반면, 다른 isoforms는 pyroptotic activity가 약화되거나 전혀 나타나지 않습니다. 전반적으로 이 연구는 Shigella IpaH7.8의 분자적 메커니즘과 GSDM의 표적화를 밝히고, pyroptotic activity에 중요한 GSDMB의 구조적 결정 요인을 보여줍니다.
