Fumarate innate immunity 유도하기 위해 mtDNA의 vesicular release를 유도한다.
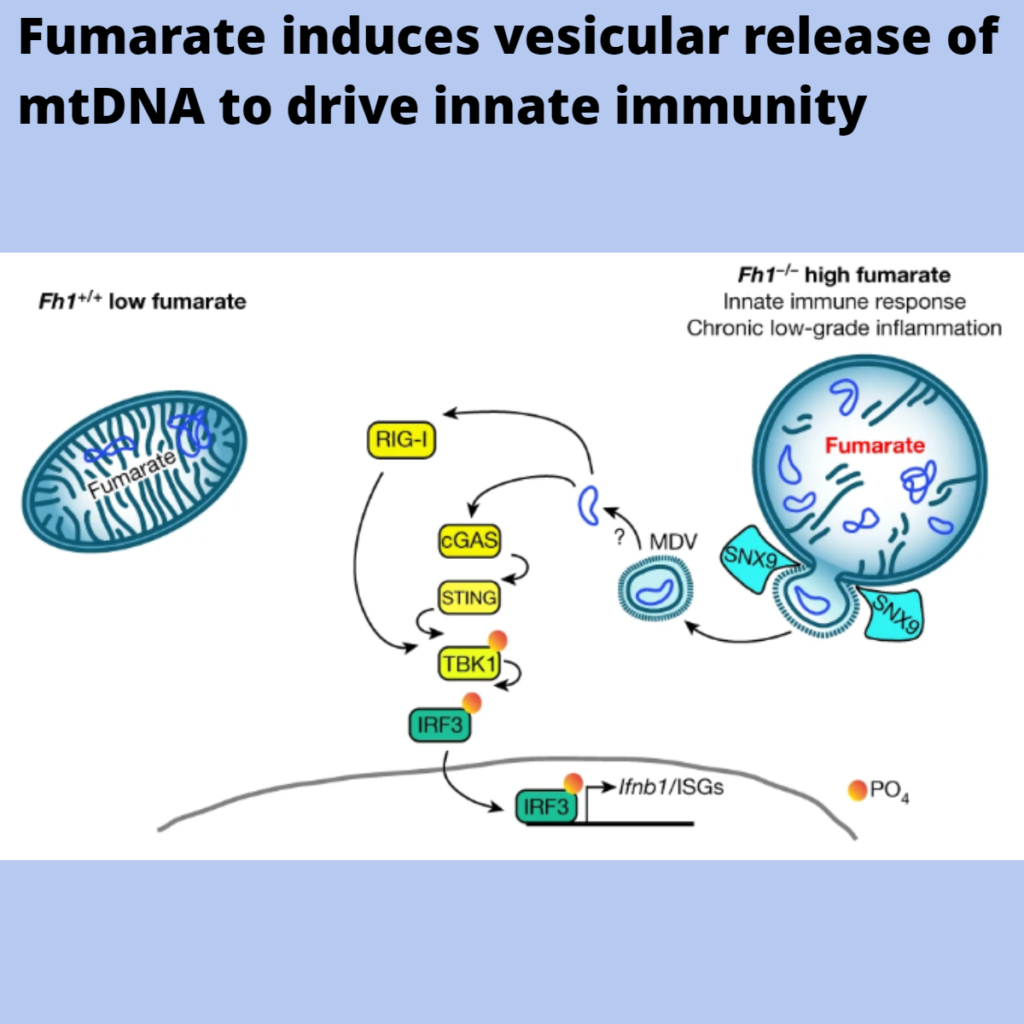
Abstract
fumarate hydratase (FH)의 Mutation은 hereditary leiomyomatosis 및 renal cell carcinoma을 유발한다. kidney에서 FH의 손실은 oncometabolite fumarate의 축적을 통해 여러 oncogenic signalling cascades를 유도한다. 그러나 FH 손실의 장기적인 결과가 설명되었지만, 급성 반응은 지금까지 조사되지 않았다.
여기서 우리는 kidney에서 FH 손실의 chronology를 연구하기 위해 유도 가능한 마우스 모델을 생성했다. 우리는 FH의 손실이 mitochondrial morphology의 초기 변화와 미토콘드리아 DNA(mtDNA)의 cytosol로의 방출로 이어지며, 여기서 interferon genes (STING)–TANK-binding kinase 1 (TBK1) pathway의 cyclic GMP–AMP synthase (cGAS)–stimulator의 활성화를 촉발하고 retinoic-acid-inducible gene I (RIG-I)에 부분적으로 의존하는 염증 반응을 자극한다는 것을 보여준다. 기계적으로, 우리는 이 표현형이 fumarate에 의해 매개되고 sorting nexin 9 (SNX9)에 의존하는 방식으로 mitochondrial-derived vesicle을 통해 선택적으로 발생한다는 것을 보여준다. 이러한 결과는 intracellular fumarate의 증가된 수준이 미토콘드리아 네트워크의 리모델링과 mitochondrial-derived vesicle의 생성을 유도하여 세포질에서 mtDNA의 방출과 이후 innate immune response의 활성화를 가능하게 한다는 것을 보여준다.
Figure
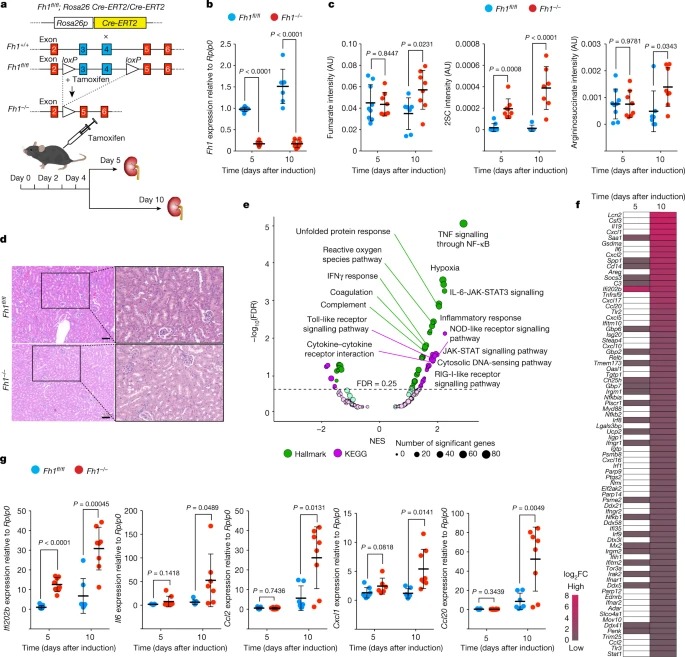
Fig. 1: adult mouse kidney에서 Fh1의 손실은 an early inflammatory response를 유발한다.
a, 유도 가능한 Fh1 knockout allele를 생성하기 위한 Genome-editing strategy.
b, wild-type control (Fh1+/+)과 Fh1- deficient (Fh1-/-) adult mouse kidney에서 Fh1 mRNA 발현 수준을 측정한 qRT-PCR.
c, liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry (LC–MS)에 의해 측정된 Fh1+/+ 및 Fh1-/- adult mouse kidney의 Metabolite abundance (normalized peak ion intensity, 임의 단위(AU)).
d, 유도 후 10일째에 Fh1+/+ 및 Fh1— adult mouse kidney의 Haematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining.
e, 유도 후 10일째에 Fh1-/- 대 Fh1+/+ kidney tissue에서 차등적으로 조절된 경로를 강조하는 GSEA의 Volcano plot.
f, 유도 후 5일차와 10일차에 Fh1-/- 대 Fh1+/+ kidney tissue에서 조절된 inflammation-related gene을 보여주는 Heat map.
g, 유도 후 5일차와 10일차에 Fh1-/- 대 Fh1+/+ kidney tissue에서 ISG의 발현 수준을 측정한 qRT-PCR.
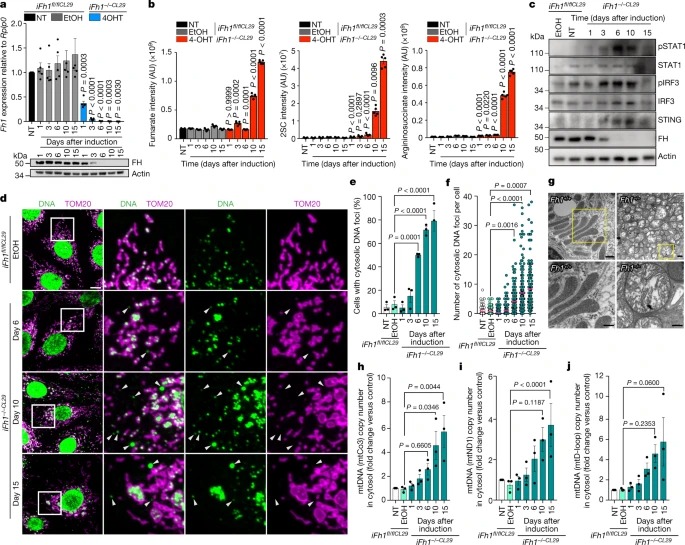
Fig. 2: Fh1-deficient cell에서 cGAS-STING 경로의 activation은 cytosolic mtDNA에 의해 유발된다.
a, 처리되지 않거나(NT) 표시된 기간 동안 vehicle (에탄올; EtOH) 또는 4-OHT(iFh1-/-CL29)로 처리 유도성 iFh1 epithelial kidney cell lines clones 29 (iFh1fl/flCL29)에서 Fh1(상단) 또는 FH 단백질(하단)의 발현 수준을 보여주는 qRT-PCR(상단) 및 immunoblots (하단).
b, LC-MS로 측정한 iFh1CL29 세포에서 fumarate(왼쪽), 2SC(중간) 및 argininosuccinate(오른쪽)의 Relative abundance (normalized peak ion intensity).
c, iFh1CL29 세포에서 특정 단백질의 Immunoblots.
d, iFh1CL29 세포에서 mitochondrial morphology (TOM20) 및 DNA foci (DNA)의 Representative confocal images.
e, f, d에서 cytosolic DNA foci (e) 및 세포당 cytosolic DNA foci의 수(f)를 나타내는 iFh1CL29 세포의 백분율.
g, Fh1+/+ 및 Fh1-/- adult mouse kidney tissue로부터의 미토콘드리아의 TEM 이미지.
h–j, 유도 후 1일에서 15일까지 iFh1CL29 세포의 isolated cytosolic fraction에서 mtCo3(h), mtND1(i) 또는 mtD-loop(j) probe를 사용하여 ddPCR에 의한 mtDNA copy number의 정량화.
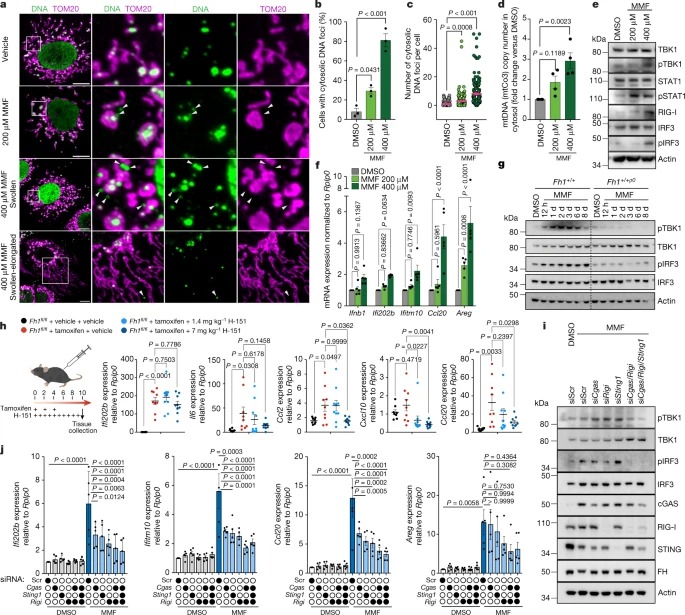
Fig. 3: Fumarate는 mitochondrial morphology의 리모델링과 mtDNA의 방출을 유도한다.
a–f, Chronic Fh1 kidney cell (cFh1fl/fl)을 200μM 또는 400μM MMF 또는 vehicle (디메틸 설폭사이드; DMSO)로 8일간 처리.
a, cFh1fl/fl 세포에서 mitochondrial morphology (TOM20) 및 DNA foci (DNA)의 Representative confocal image.
b,c, a에서 cytosolic DNA foci (b) 및 세포당 cytosolic DNA foci의 수(c)를 나타내는 cFh1fl/fl 세포의 백분율.
d, cFh1fl/fl 세포의 분리된 cytosolic fraction으로부터 mtCo3 probe를 사용하여 ddPCR에 의한 mtDNA copy number의 정량화.
e, cFh1fl/fl 세포에서 특정 단백질의 Immunoblots.
f, qRT-PCR로 측정한 cFh1fl/fl 세포에서의 ISG 발현.
g, iFh1fl/flCL29 및 mtDNA-depleted iFh1fl/flCL29ρ0 세포에서 특정 단백질의 Immunoblots.
h, qRT-PCR로 측정한 STING inhibitor H-151로 처리한 mouse kidney tissue에서 ISG 패널의 mRNA 발현.
i,j, 400 μM MMF 또는 DMSO로 8일 동안 처리하고 표시된 siRNA(Scr, scramble)로 transfected된 cFh1fl/fl 세포에서 qRT-PCR(j)로 측정한 특정 단백질(i) 및 ISG 발현의 Immunoblots.
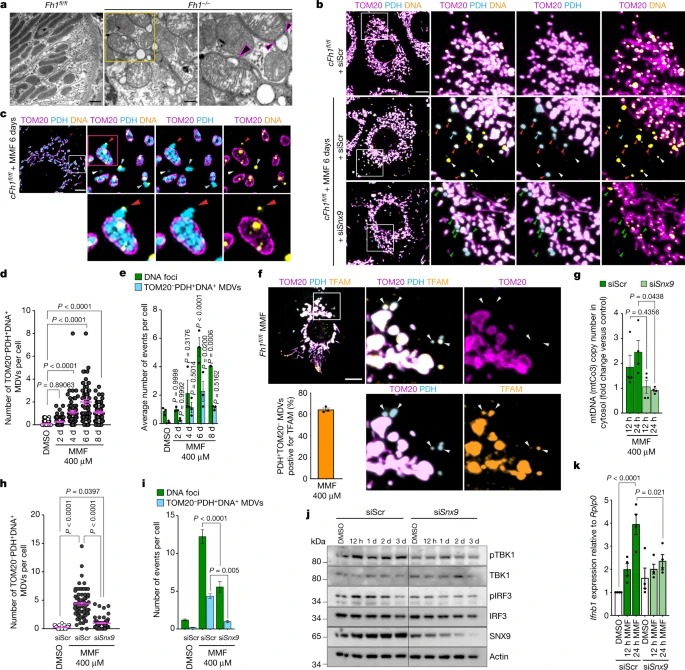
Fig. 4: mtDNA는 MDV에 의해 cytosol로 전달된다.
a, Fh1+/+ 및 Fh1-/- mouse kidney의 TEM 이미지는 미토콘드리아 표면(검은 화살촉)에서 potential vesicle budding을 보여준다.
b, 표시된 siRNA로 transfected된 cFh1fl/fl 세포의 Representative confocal image.
c, MMF- treated cFh1fl/fl 세포의 대표적인 Representative N-structured illumination microscopy (N-SIM) super-resolution image.
d,e, TOM20-PDH+DNA+ MDV의 정량화(d), cFh1fl/fl 세포에서 cytosolic DNA foci (e)와 비교.
f, MMF- treated cFh1fl/fl 세포의 Representative confocal image.
g, MMF 처리된 cFh1fl/fl 세포(12시간 또는 24시간)의 분리된 cytosolic fraction으로부터 mtCo3 probe를 사용하고 표시된 siRNA로 pre-transfected된 ddPCR에 의한 mtDNA copy number의 정량화.
h,i, TOM20-PDH+DNA+ MDV의 정량화(h) 및 MMF 처리 cFh1fl/fl 세포에서 cytosolic DNA foci (i)와 비교하고 표시된 siRNA로 pre-transfected.
j,k, 표시된 siRNA로 transfected되고 표시된 기간 동안 MMF로 처리된 cFh1fl/fl 세포에서 qRT-PCR(k)로 측정된 특정 단백질(j) 및 Ifnb1 mRNA 발현의 Immunoblots.
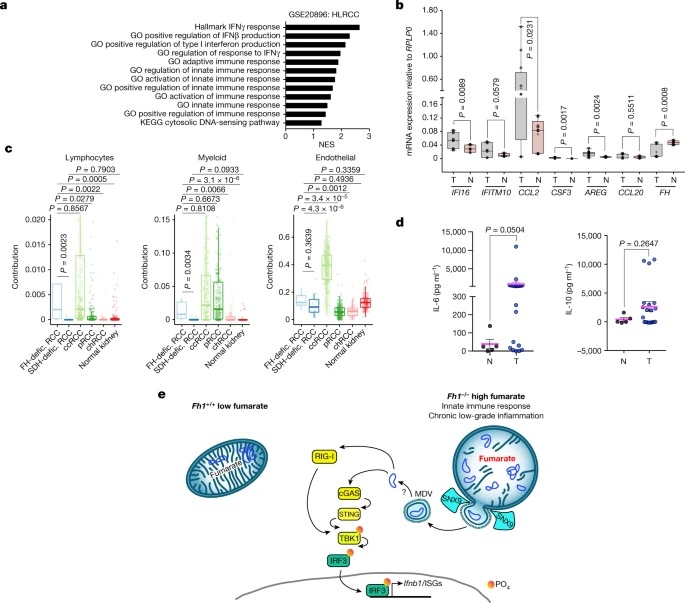
Fig. 5: FH-deficient tumour tissue는 inflammatory signature를 특징으로 한다.
a, HLRCC 종양 대 정상 조직의 유전자 발현 프로파일의 GSEA.
b, qRT-PCR로 측정한 HLRCC 종양 대 정상 조직에서 ISG 패널의 mRNA 발현.
c, FH-deficient RCC, SDH-deficient RCC 및 TCGA의 일반적인 RCC 하위 유형의 bulk RNA sequencing 데이터 세트의 Cellular composition.
d, ELISA(enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay)에 의해 측정된 HLRCC 종양 대 정상 조직에서의 IL-6 및 IL-10의 수준.
e, Schematic of the pathway.
Disscussion
이 연구에서, 우리는 fumarate이 미토콘드리아 네트워크의 리모델링, 세포질로의 mtDNA의 방출, 그리고 선천적인 면역 반응의 활성화를 초래한다는 것을 보여주었다(그림 5e). 이 반응은 빠르게 나타나지만, 시간이 지남에 따라 지속되며, HLRCC 환자에서도 관찰되며, HLRCC에서 mtDNA 방출, 만성 염증 및 종양 발생 사이에 직접적인 상호 작용이 있음을 시사한다.
우리의 결과는 cGAS 외에도 짧은 viral double-stranded RNA와 DNA를 인식할 수 있고 STING sensing pathway에 연결된 RIG-I도 역할을 한다는 것을 보여준다. 그러나 Mavs의 silencing은 TBK1-IRF3 신호 전달에 아무런 영향을 미치지 않았으며, 이는 RIG-I가 비표준적인 기능을 가지고 있음을 시사한다.
비록 VDAC1 oligomerization, mitochondrial permeability transition pore 및 BAX 및 BAK pores의 개방이 mtDNA 방출을 허용하도록 제안되었지만, mtDNA는 막 무결성을 보존하는 대체 메커니즘인 SNX9-dependent MDV를 통해 세포질로 운반된다는 것을 발견했다(그림 5e).
전반적으로, 이 연구는 미토콘드리아가 선천적 면역 반응에 어떻게 영향을 미칠 수 있는지에 대한 우리의 이해를 확장하고 metabolite-driven immunopathology에 대한 추가 조사의 근거를 제공한다.
