Ensembles of endothelial and mural cells promote angiogenesis in prenatal human brain endothelial과 mural cell의 앙상블은 태아기 인간의 뇌에서 angiogenesis를 촉진한다.
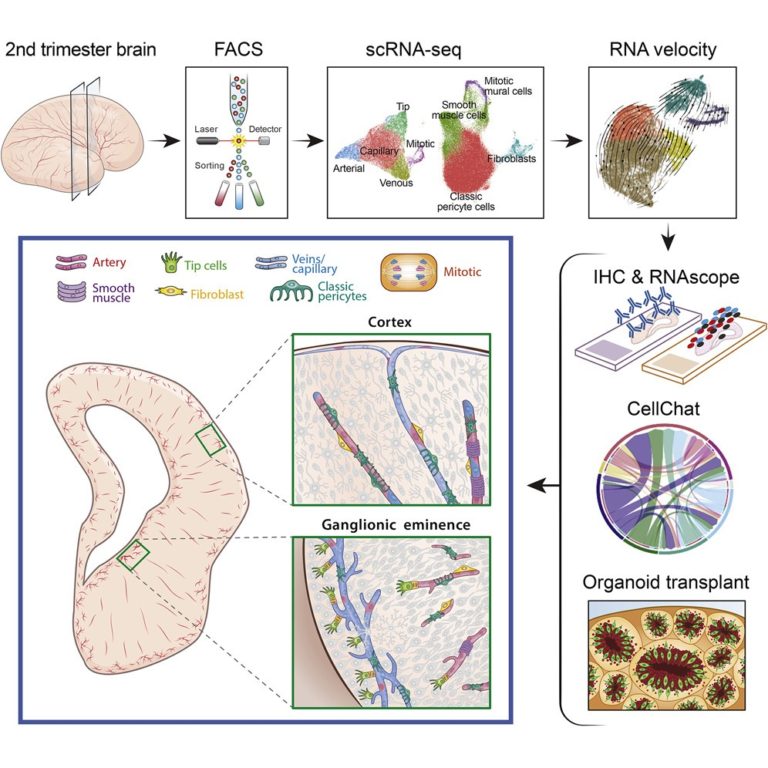
Angiogenesis와 neurogenesis 사이의 상호작용은 embryonic brain 발달을 조절한다. 그러나 특히 prenatal(태아기) 인간의 뇌에서 vascular cell maturation 단계에 대한 포괄적인 이해가 부족하다.
fluorescence-activated cell sorting, single-cell transcriptomics, histological and ultrastructural analysis를 사용하여, 우리는 endothelial and mural cell subtype의 앙상블이 임신 중기 동안 brain vasculature를 타일링한다는 것을 보여준다. 이러한 혈관 세포는 뚜렷한 발달 궤적을 따르고, cell-cell communication과 maturation을 용이하게 하기 위해 collagen, laminin, and midkine을 포함한 다양한 신호 전달 메커니즘을 사용한다. 흥미롭게도, 우리의 결과는 endothelial cell의 subtype인 tip cell가 active neurogenesis site인 ventricular zone 근처에서 매우 풍부하다는 것을 보여준다. 이러한 관찰과 일관되게, cortical organoid에 이식된 prenatal vascular cell은 tip cell를 선호하고, neurogenesis를 촉진하며, 세포 스트레스를 감소시키는 restricted lineage potential을 나타낸다.
우리의 결과는 인간의 뇌 발달의 중요한 기간 동안 vascular maturation에 대한 중요한 메커니즘을 밝혀낸다.

![Read more about the article [Cell Metabolism] Vps37a regulates hepatic glucose production by controlling glucagon receptor localization to endosomes](https://scienceeasyview.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/11/Vps37a-regulates-hepatic-glucose-production-by-controlling-glucagon-receptor-localization-to-endosomes-GA-300x300.jpg)