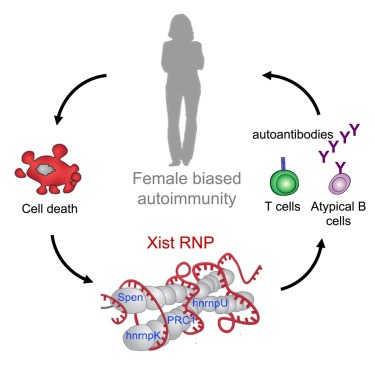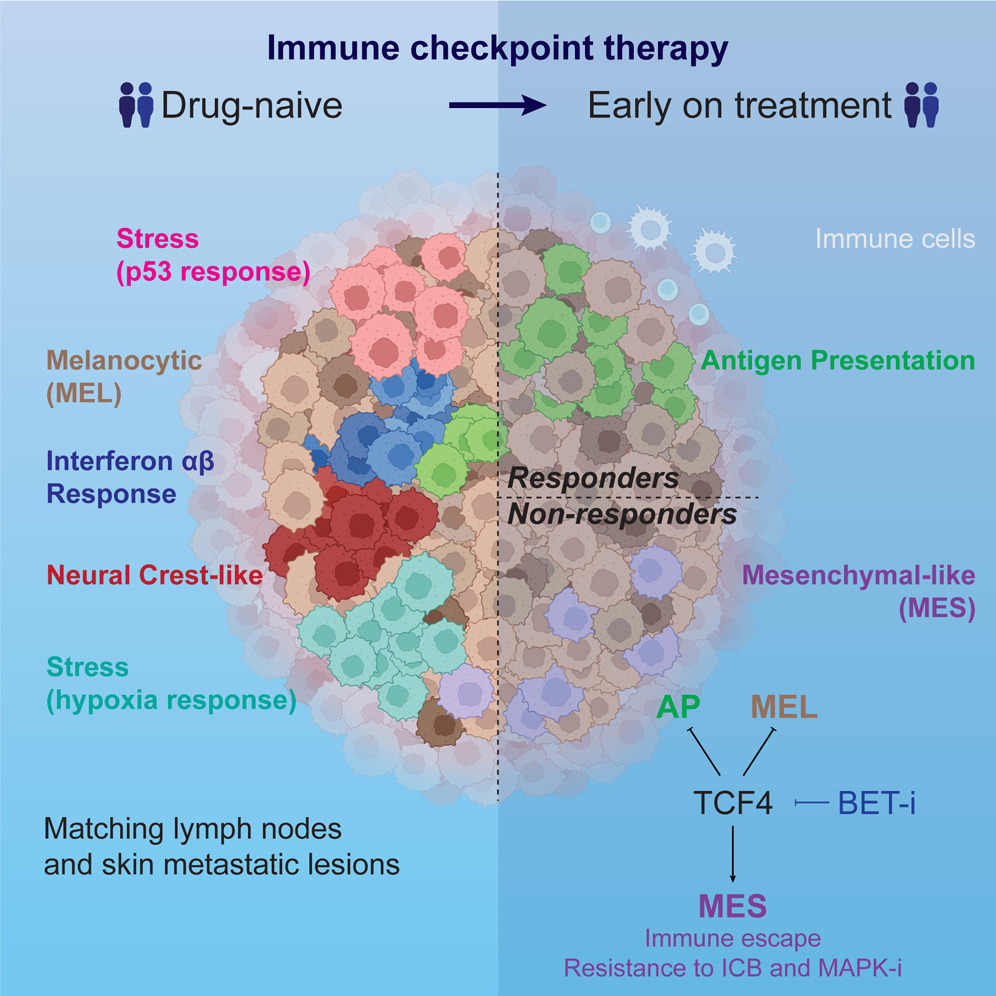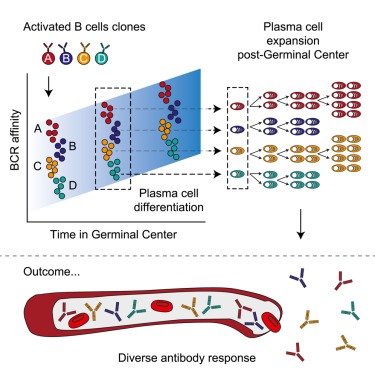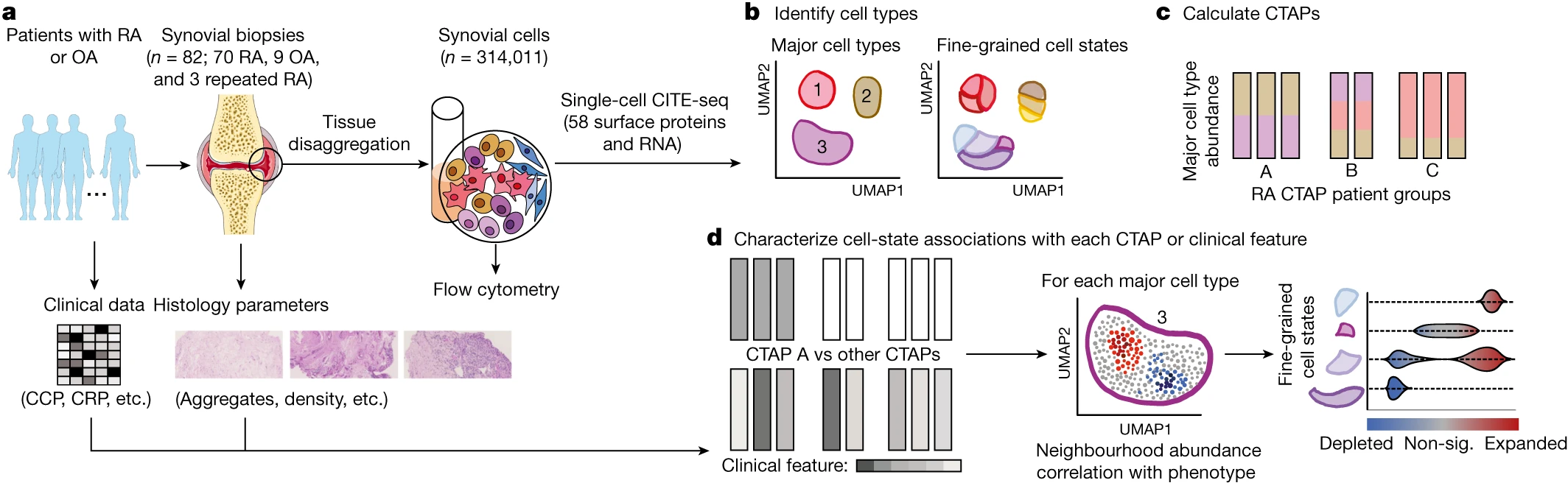
a,b, WT (n = 27) and Akita (n = 19) mice infected with 200 plaque-forming units (pfu) PR8, log-rank Mantel–Cox test. a, Survival. Inset, lung PR8 RNA 10 d.p.i., WT (n = 16) and Akita (n = 7) mice infected with 50 pfu PR8, two-sided Mann–Whitney U-test. b, Lung NP34-tetramer+CD8+ T cells, two-sided Mann–Whitney U-test. c,d, Mice infected with 50 pfu PR8, treated with insulin (Ins)/phosphate-buffered saline (PBS): WT+PBS (n = 16), WT+Ins (n = 15), Akita+PBS (n = 13), Akita+Ins (n = 15), Kruskal–Wallis test with Dunn’s correction, two pooled experiments. c, Lung PR8 RNA. d, Lung NP34-tetramer+CD8+ T cells. e,f, Mice infected with 200 pfu PR8, administered STZ (n = 18 for e, n = 9 for f) or PBS (n = 30 for e, n = 20 for f). e, Survival, log-rank Mantel–Cox test. Inset, lung PR8 RNA 10 d.p.i., mice infected with 50 pfu PR8, administered STZ (n = 9) or PBS (n = 20), two-sided Mann–Whitney U-test. f, Lung NP34-tetramer+CD8+ T cells, two-sided Mann–Whitney U-test. g,h, Mice infected with 50 pfu PR8, administered STZ or PBS, treated with Ins/PBS: PBS+PBS (n = 27 for g, n = 19 for h), PBS+Ins (n = 19 for g, n = 15 for h), STZ+PBS (n = 10 for g, n = 4 for h), STZ+Ins (n = 17 for g, n = 11 for h), Kruskal–Wallis test with Dunn’s correction. g, PR8 RNA, three pooled experiments. h, Lung NP34-tetramer+CD8+ T cells, two pooled experiments. i,j, Db/Db (n = 9 for i, n = 10 for j) and WT (n = 10 for i, n = 15 for j) mice infected with 200 pfu PR8. i, Survival, log-rank Mantel–Cox test. Inset, lung PR8 RNA 10 d.p.i., WT (n = 20) and Db/Db (n = 10) mice infected with 50 pfu PR8, three pooled experiments, two-sided Mann–Whitney U-test. j, NP34-tetramer+CD8+ T cells, two-sided Mann–Whitney U-test. k, Survival, WT (n = 15) and Akita (n = 18) mice infected with 200 pfu PVM, log-rank Mantel–Cox test. Inset, lung PVM RNA 10 d.p.i., WT (n = 15) and Akita (n = 17) mice infected with 50 pfu PVM, two-sided Mann–Whitney U-test. All P values are indicated in Supplementary Table 1. All data mean+s.e.m. a.u., Arbitrary units.
폐 수지상 세포 대사는 당뇨병의 바이러스 감염에 대한 취약성의 근간을 이룸 Abstract 당뇨병 환자는 인플루엔자 및 SARS-CoV-2를 포함한 호흡기 바이러스 감염에 생명을 잃을 위험이 있으며, 그 메커니즘은 아직 알려지지 않았다.…