The selection landscape and genetic legacy of ancient Eurasians
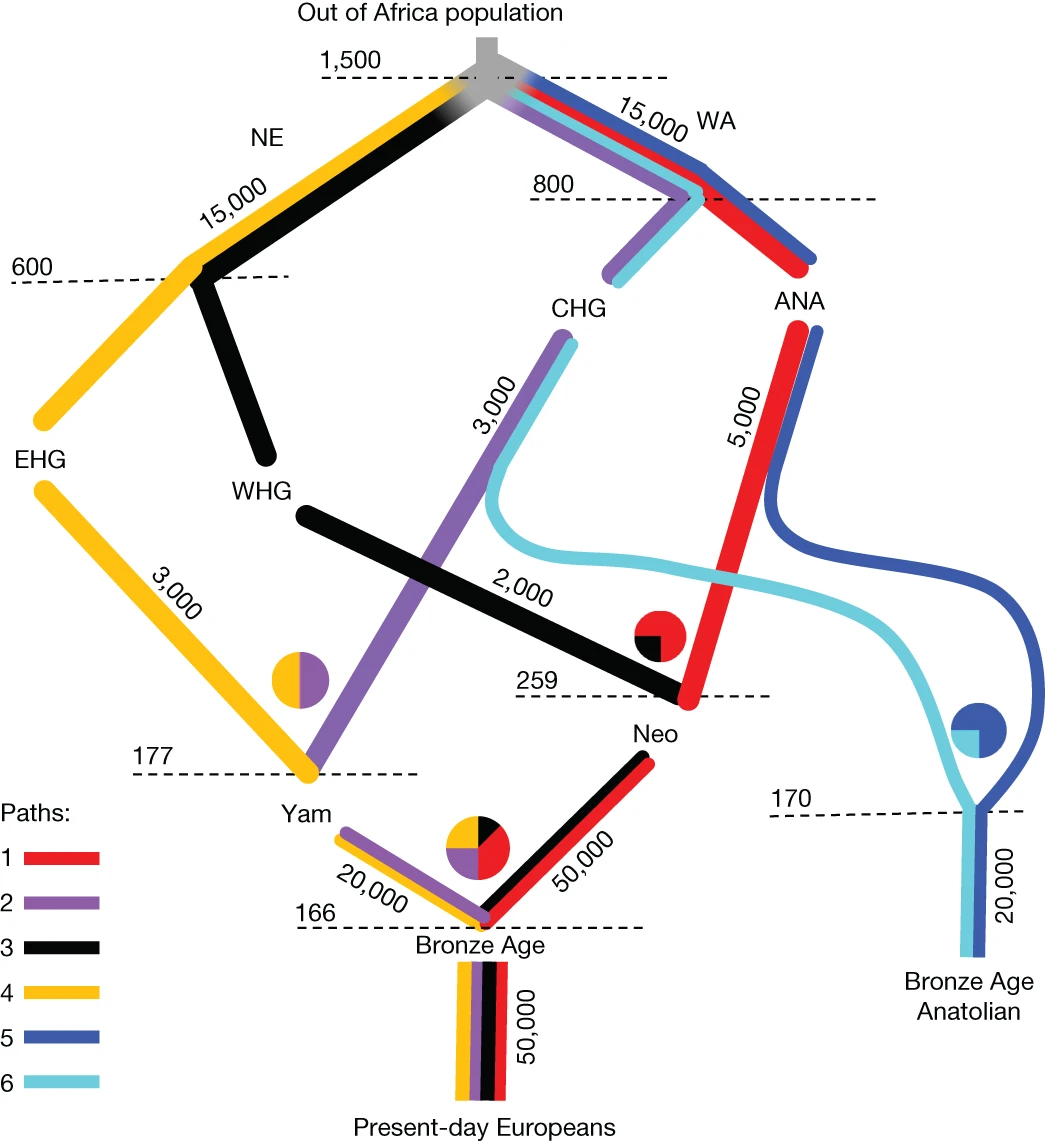
고대 유라시안의 selection landscape와 유전적 유산 Abstract *홀로세(Holocene)는 인간 진화에서 가장 중요한 변화를 포함하고 있으며, 현대 인구의 식단, 신체 및 정신 건강에 광범위한 영향을 미친 시기이다. 우리는 1,600개 이상의 추정된…

고대 유라시안의 selection landscape와 유전적 유산 Abstract *홀로세(Holocene)는 인간 진화에서 가장 중요한 변화를 포함하고 있으며, 현대 인구의 식단, 신체 및 정신 건강에 광범위한 영향을 미친 시기이다. 우리는 1,600개 이상의 추정된…
SPLASH: 생물학적 발견을 통합하는 통계적이고 참조 없는 유전적 알고리즘 Abstract 현재의 유전체 분석 워크플로우는 대체로 참조 서열과의 정렬(alignment)을 필요로 하며, 이는 발견을 제한합니다. 우리는 통합적인 패러다임인 SPLASH (Statistically Primary aLignment…
전체 mouse brain의 세포 유형에 대한 고해상도 transcriptomic과 spatial atlas Abstract 성인 쥐 뇌는 수백만에서 수십억 개의 세포로 구성되어 있으며, 이들은 특정한 spatial 분포 패턴과 구조적, 기능적 특성을 가진 많은…
류마티스 관절염 *윤활막(synovium)의 세부 분석으로 염증성 subtype을 정의 Abstract 류마티스 관절염은 관절의 염증과 파괴를 일으키는 전형적인 자가면역 질환이다. 현재 류마티스 관절염에 대한 치료법은 없으며, 치료의 효과가 환자에 따라 다르다는 점에서…
11가지 tumour 유형에서 암으로 변화하는 과정의 epigenetic 조절 Abstract Chromatin accessibility는 유전자 발현 조절 및 세포 정체성(Cellular identity)에 필수적이며, accessibility의 변화는 암의 시작, 진행 및 metastasis를 촉진하는 것과 관련이 있다.…
UK Biobank의 genetics 및 health의 Plasma proteomic associations. Abstract Pharma Proteomics Project는 54,219명의 UK Biobank participants의 plasma proteomic profiles을 특성화하는 precompetitive biopharmaceutical consortium입니다. 여기에서는 기술 및 생물학적 검증, proteomic disease…
Cooperative assembly로 regulatory specificity와 long-term genetic circuit stability 제공 Abstract eukaryotic transcriptional regulation의 보편적인 특징은 transcription factors (TF)와 DNA cis-regulatory motifs 간의 cooperative self-assembly입니다. 이 전략은 상호 작용이 약하고 특이성이…
인간의 mtDNA copy number와 heteroplasm의 핵 유전적 제어 Abstract 미토콘드리아 DNA (mtDNA)는 산화적 인산화에 필요한 DNA로 모계 유전과 높은 copy number를 가진 유전체입니다. Heteroplasmy는 개인의 mtDNA 대립유전자 혼합물의 존재를 의미하며…
녹내장과 대장암에 대한 가장 높은 유전적 위험을 가진 loci의 기초가 되는 repeat polymorphism Abstract 인간 유전체의 많은 영역은 variable numbers of tandem repeat (VNTR)으로 인해 개인마다 길이가 다릅니다. VNTR 유전체…
인구 간 SARS-CoV-2에 대한 single-cell 반응의 차이 분석 Abstract 서로 다른 인구는 각자 SARS-CoV-2 감염 이후 나타나는 임상적인 증상에 차이를 보이며, 그 유전적 및 면역학적 기반은 최근에 들어 밝혀지기 시작했습니다.…