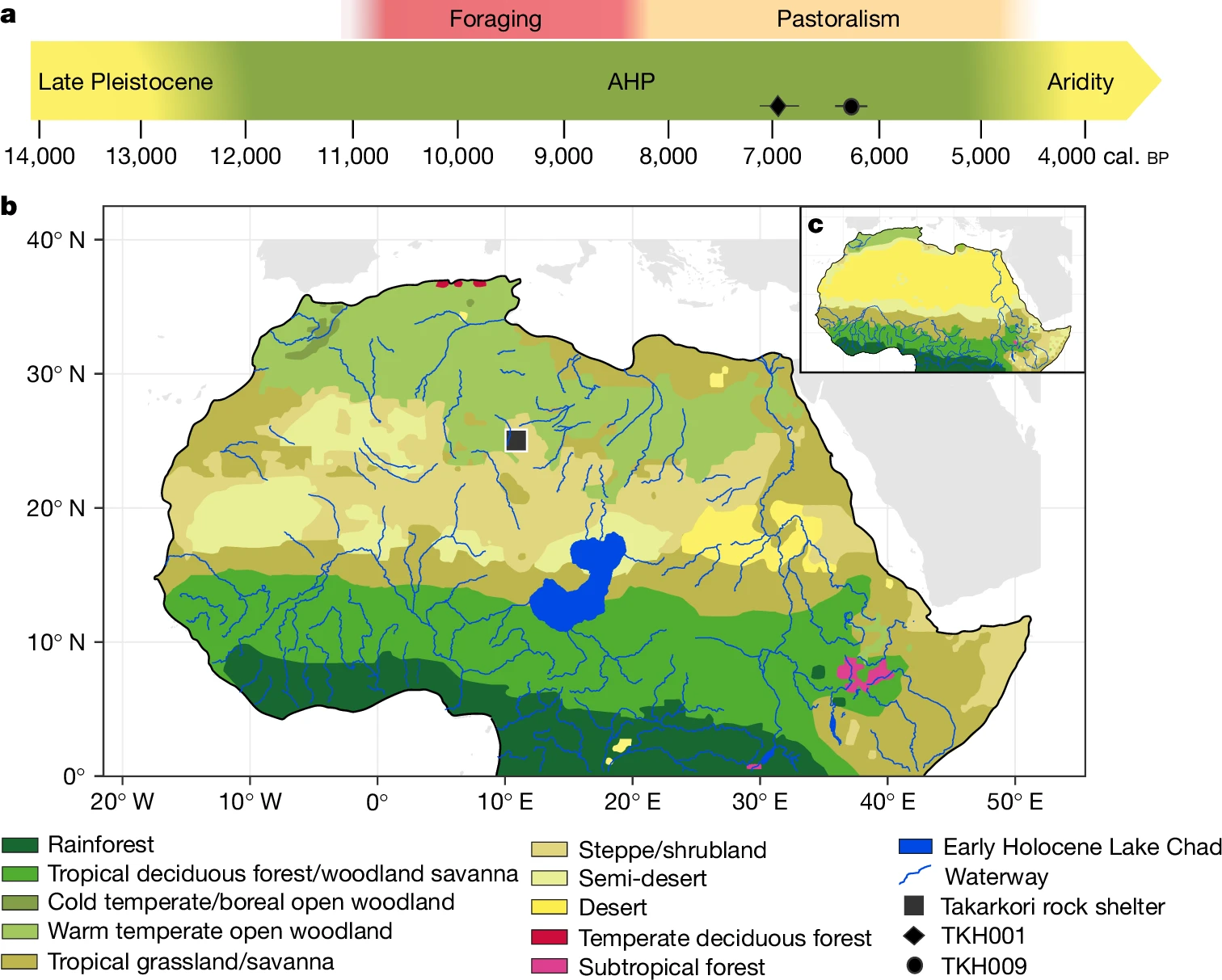
Ancient DNA from the Green Sahara reveals ancestral North African lineage
Green Sahara의 고대 DNA는 고대 North African 혈통을 밝혀낸다. Abstract 오늘날 가장 건조한 지역 중 하나인 사하라는 약 14,500년 전부터 5,000년 전까지 지속된 아프리카 습윤기 동안 녹색 초원 지대로 변모하여,…

Green Sahara의 고대 DNA는 고대 North African 혈통을 밝혀낸다. Abstract 오늘날 가장 건조한 지역 중 하나인 사하라는 약 14,500년 전부터 5,000년 전까지 지속된 아프리카 습윤기 동안 녹색 초원 지대로 변모하여,…
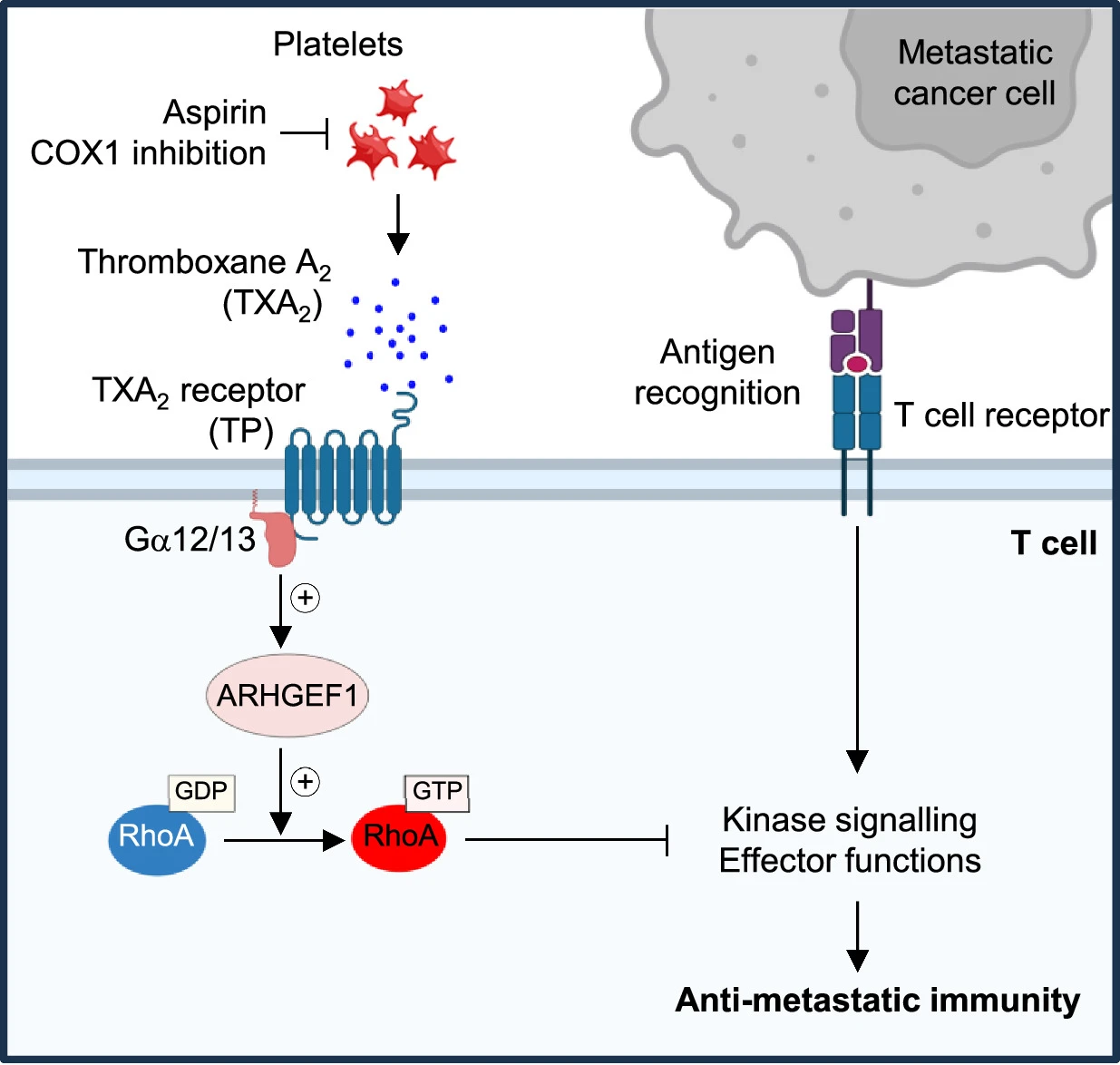
아스피린은 T 세포 면역을 억제하는 혈소판 TXA2 제한을 통해 전이를 방지한다 Abstract 전이는 암세포가 원발성 종양에서 멀리 떨어진 장기로 퍼지는 현상으로, 전 세계적으로 암 사망의 90%의 원인이 된다. 전이하는 암세포는…
인체 골격 발달의 기능적 유전체학과 키 유전성의 패턴 분석 Abstract 키의 변이는 긴뼈 성장판을 구성하는 연골세포 (연골모세포)의 조절 변화에 기인합니다. 현재까지 우리는 인체 골격에서 채취한 연골모세포의 후성유전학적 조절과 유전자 발현에…
뇌 노화에서의 세포 근접 효과를 ‘공간 전사체 시계’로 밝혀내다 Abstract 노화는 인지 기능 저하와 신경퇴행성 질환 위험 증가와 밀접한 관련이 있습니다. 뇌의 노화는 복잡하며, 여러 세포 수준의 변화가 동반됩니다. 그러나…
청동기 시대 치즈에서 드러난 인간-Lactobacillus 상호작용의 진화 역사 Abstract 발효 유제품 섭취의 오랜 역사에도 불구하고, 발효 미생물이 인류 역사 동안 어떻게 사용되고 진화했는지에 대해서는 거의 알려져 있지 않습니다. 이 연구에서는…
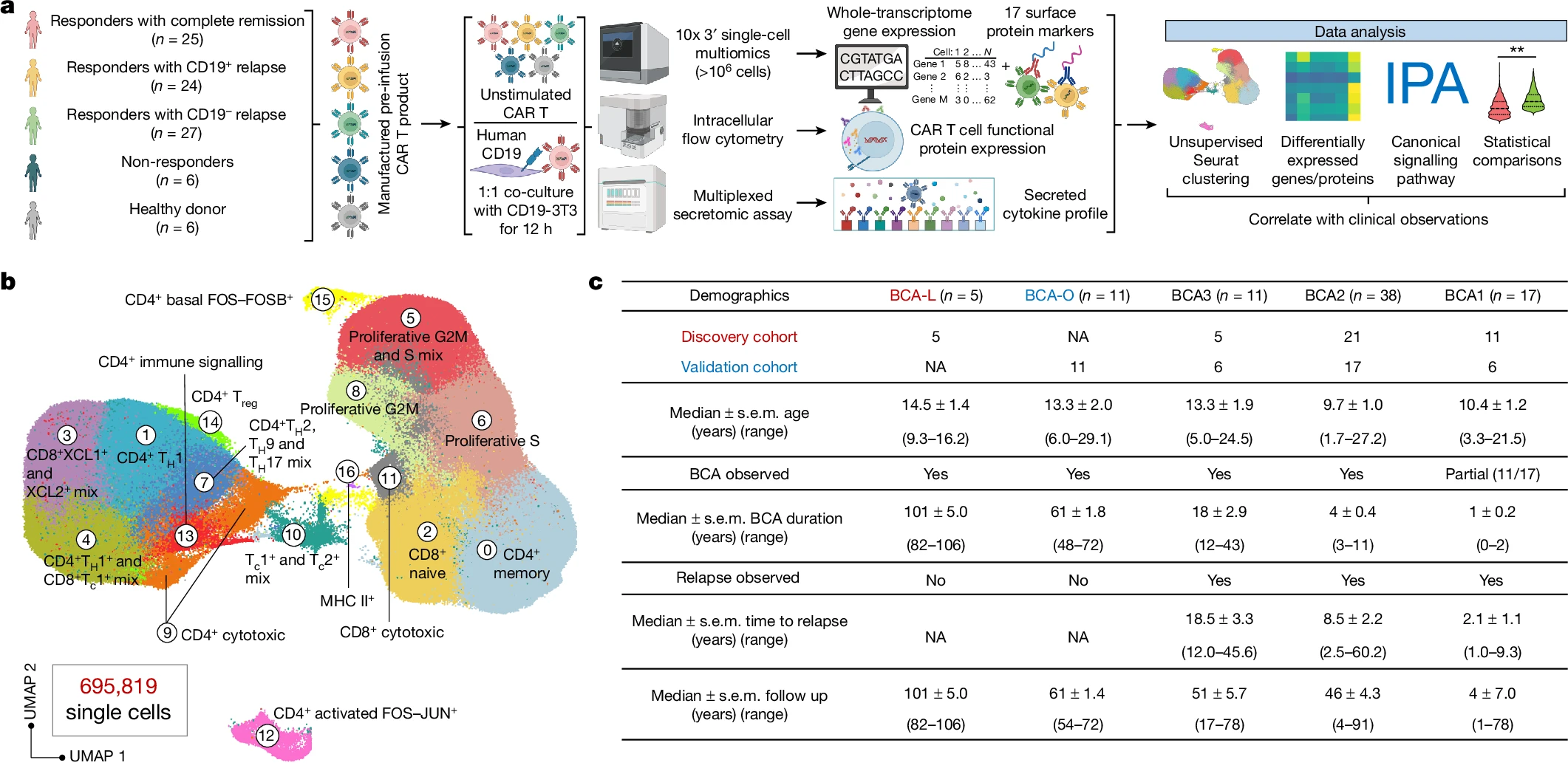
Single-cell CAR T 아틀라스가 8-year leukaemia remission에서 type 2 function을 밝혀낸다 Abstract Acute lymphocytic leukaemia(ALL)에 대한 chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cell 치료의 높은 반응률에도 불구하고 약 50%의 환자가 첫해…
Amylase 유전자좌에서 재발생하는 진화와 선택에 의한 구조적 다양성 형성 Abstract 농업의 채택은 인간 집단에서 녹말이 풍부한 식단으로의 급격한 전환을 초래했습니다. Amylase 유전자는 녹말 소화를 돕는데, 녹말 섭취량이 많은 현대 인구…
대장암에서의 예후 예측 유전체 및 전사체 시그니처 Abstract 대장암은 핵심 암 경로에 있는 드라이버 유전자에 영향을 미치는 일련의 체세포 유전체 변이에 의해 발생합니다. 이 연구에서는 암을 유발하는 체세포 돌연변이의 기능적…
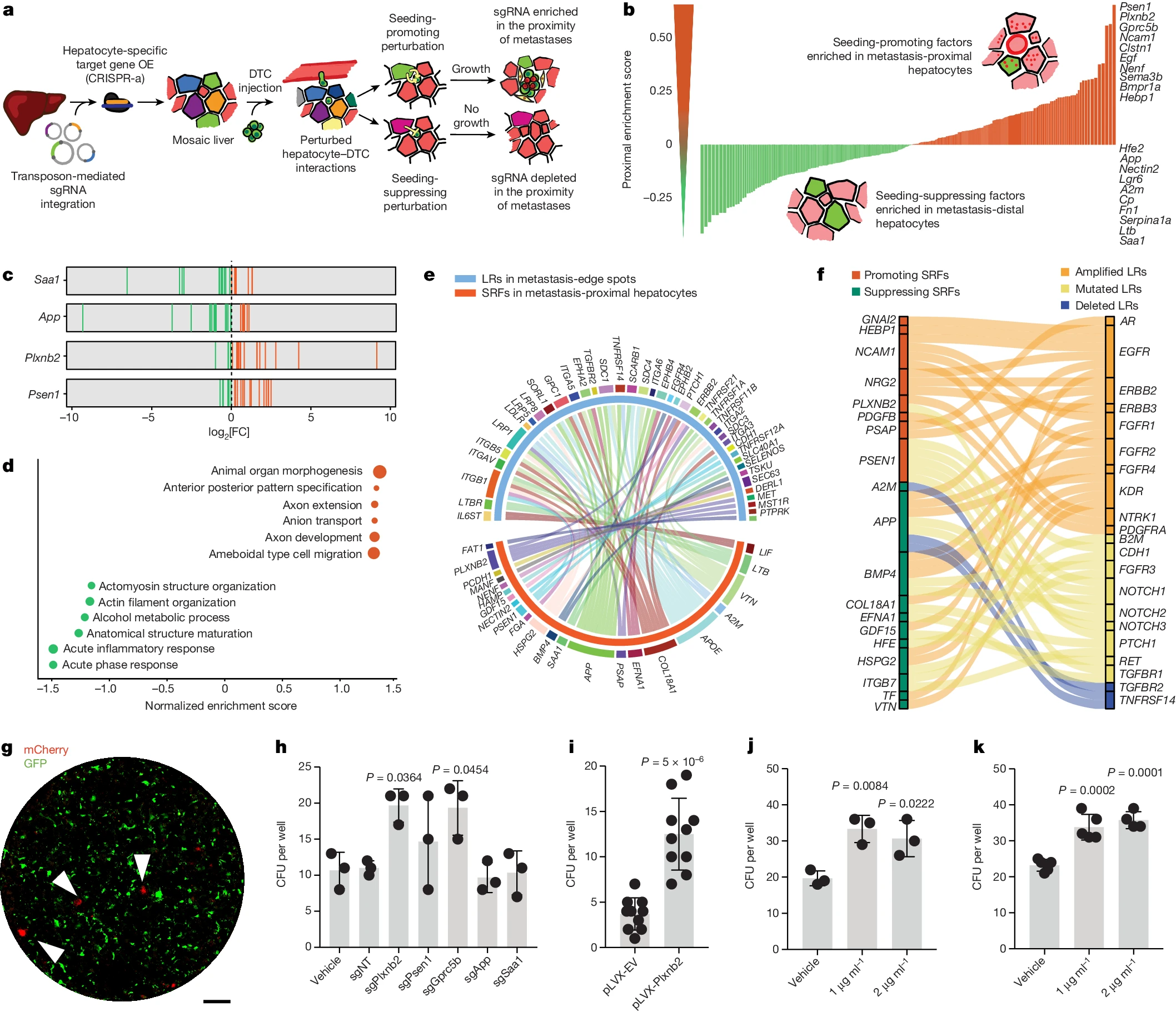
In vivo 상호작용 screening은 전이에 대한 간 유래 constraints를 밝혀낸다 Abstract 전이된 암 세포 중 단 0.02%만이 *명확한 전이(overt metastasis)를 일으킬(seed) 수 있는 것으로 추정된다. 이는 전이의 seeding에 대한 환경적…
인체 SARS-CoV-2 감염 모델을 통해 국소 및 전신 면역 반응 역학을 밝히다 Abstract COVID-19 팬데믹은 여전히 지속 중이며 위협적이지만, 이 질병에 대한 초기 세포 반응의 역학에 대한 이해는 제한적입니다. 이…