Satellite mapping reveals extensive industrial activity at sea
Satellite mapping을 통해 바다에서 발생하는 광범위한 산업 활동을 드러내다 Abstract 세계 인구는 식량, 에너지 생산, 그리고 국제 무역에 대해 점점 더 해양에 의존하고 있지만, 해양에서의 인간 활동은 잘 정량화되지 않았습니다.…
Satellite mapping을 통해 바다에서 발생하는 광범위한 산업 활동을 드러내다 Abstract 세계 인구는 식량, 에너지 생산, 그리고 국제 무역에 대해 점점 더 해양에 의존하고 있지만, 해양에서의 인간 활동은 잘 정량화되지 않았습니다.…
생명체의 유전 코드에 α,α-distributed & β-linked monomers를 추가하다 Abstract 생명체의 세포 내 *유전 부호(genetic code)는 수백 가지의 비천연 아미노산(non-canonical amino acids)을 단백질에 부위별로 통합할 수 있도록 재조정되었으며, 코돈 조합을 통해…
빙하기 이후 유라시아 서부의 인구유전체학 Abstract 서부 유라시아는 *홀로세(Holocene) 동안 여러 차례 대규모 인류 이주를 겪었습니다. 이 연구에서는 이러한 이주가 대륙 간에 미친 영향을 조사하기 위해, 유라시아 북부와 서부에서 주로…
인간 유전자가 장내 미생물 구조 변이를 조절하는 방법 Abstract 인간 유전자가 장내 미생물 다양성 및 특정 분류군의 풍부성에 미치는 영향은 이미 잘 알려져 있지만, 인간 유전자가 장내 미생물의 유전적 다양성을…
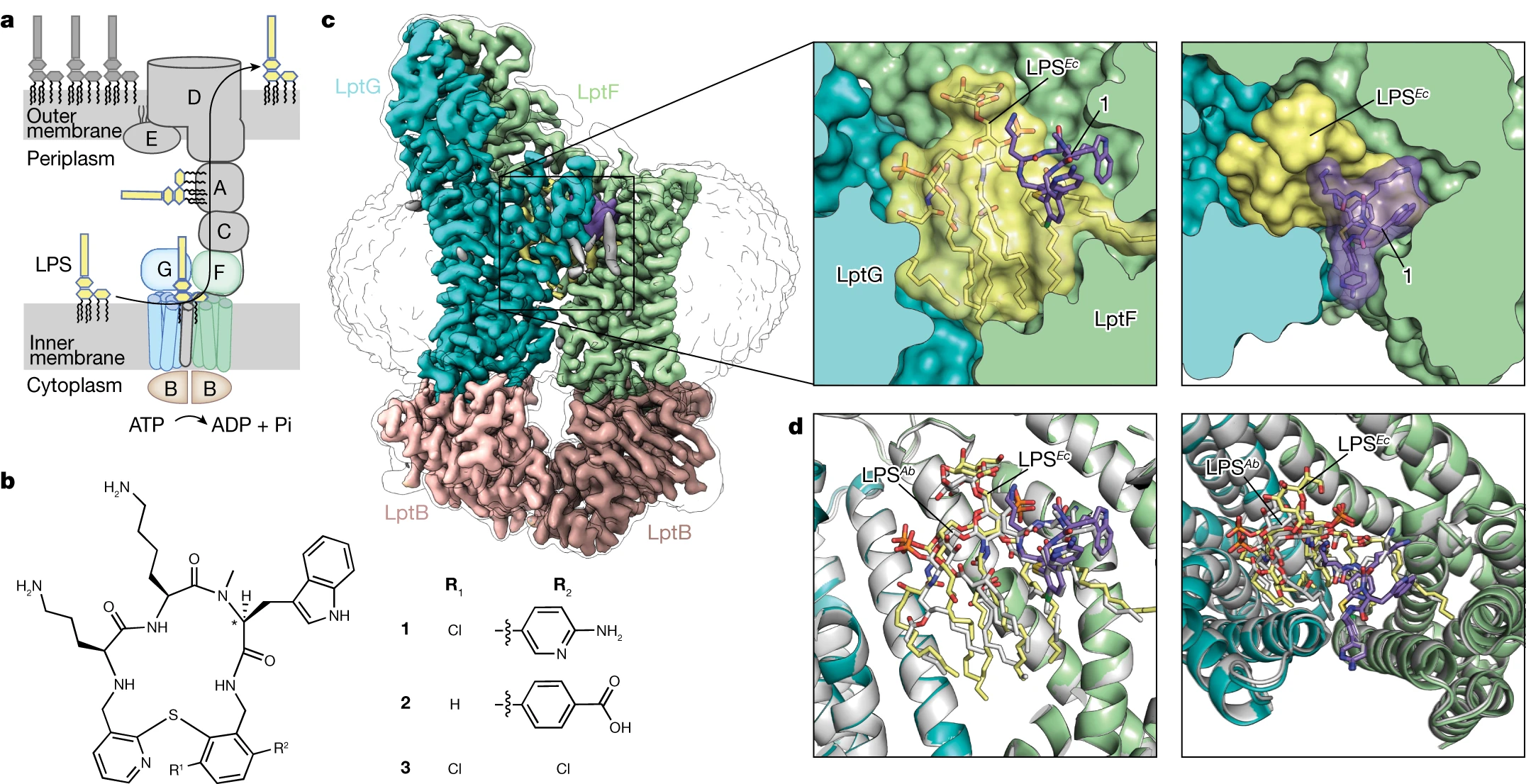
LPS를 세포막 간 transporter에 가두는 새로운 항생제 Abstract Gram-negative 박테리아의 세포질 막은 외부 막에 의해 둘러싸여 있는데, 이 외부 막은 대부분의 항생제의 진입을 막아서 박테리아를 죽이기 어렵게 만든다. 외부 막에…
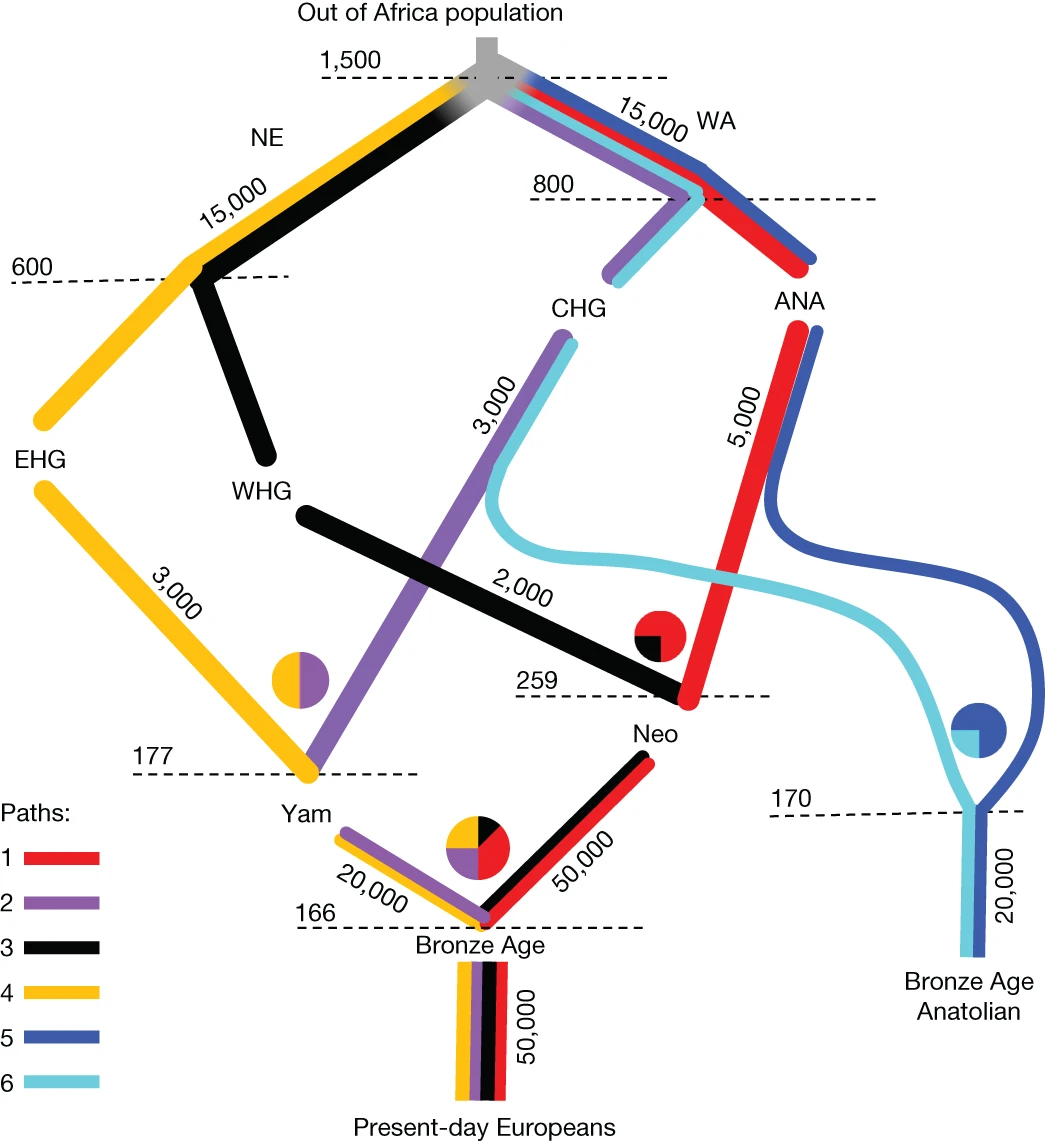
고대 유라시안의 selection landscape와 유전적 유산 Abstract *홀로세(Holocene)는 인간 진화에서 가장 중요한 변화를 포함하고 있으며, 현대 인구의 식단, 신체 및 정신 건강에 광범위한 영향을 미친 시기이다. 우리는 1,600개 이상의 추정된…
성체 생쥐 뇌의 Single-cell DNA 메틸옴 및 3D 다중-오믹스 아틀라스 Abstract Cytosine DNA 메틸화는 뇌 발달에 필수적이며 다양한 신경학적 장애와 관련이 있습니다. 전체 뇌에서 DNA 메틸화 다양성을 공간적 맥락에서 이해하는…
혈장 프로테옴에서의 장기 노화 signature이 건강과 질병에 대한 정보를 제공합니다 Abstract 동물 연구에 따르면 개체 및 개체의 장기마다 노화가 다르게 나타난다고 합니다[1-4]. 하지만 이 현상이 인간에게도 해당되는지, 그리고 이것이 연령…
영양실조 어린이를 위한 마이크로바이옴 지향 식품에서의 생물활성 다당류 Abstract 최근의 증거에 따르면, 출생 후 장내 미생물군의 발달 장애가 어린이의 영양실조에 기여할 수 있다는 것이 밝혀지고 있다. 본 연구에서는 *마이크로바이옴 지향…
전체 mouse brain의 세포 유형에 대한 고해상도 transcriptomic과 spatial atlas Abstract 성인 쥐 뇌는 수백만에서 수십억 개의 세포로 구성되어 있으며, 이들은 특정한 spatial 분포 패턴과 구조적, 기능적 특성을 가진 많은…