Evolutionary trajectories of small cell lung cancer under therapy
치료 중 소세포 폐암의 진화 과정 Abstract 소세포 폐암(Small cell lung cancer; SCLC)은 화학요법에 대해 뚜렷한 민감성을 보이는 동시에, 빠르게 재발하는 경향이 있지만, 이와 관련된 진화적 과정은 아직 명확히 알려지지…
치료 중 소세포 폐암의 진화 과정 Abstract 소세포 폐암(Small cell lung cancer; SCLC)은 화학요법에 대해 뚜렷한 민감성을 보이는 동시에, 빠르게 재발하는 경향이 있지만, 이와 관련된 진화적 과정은 아직 명확히 알려지지…
알츠하이머병 미세아교세포에서 지질 방울을 손상시키는 APOE4/4 연관성 Abstract 알츠하이머병에 대한 여러 유전적 위험 요소는 지질 대사에 관여하는 유전자들을 시사하며, 이러한 지질 유전자들 중 많은 수가 신경교세포에서 고발현됩니다. 그러나 신경교세포의 지질…
초가산적 협력 Abstract 이 연구는 인간의 일회성(one-shot) 협력에 대한 진화론적 설명을 제공하려는 시도에서 출발합니다. 이 설명은 반복적인 상호작용과 집단 간 경쟁이라는 두 가지 메커니즘에 초점을 맞춥니다. 이 논문에서는 모델과 행동…
아마존 열대우림, 위기 전환점에 직면하다 Abstract 아마존 열대우림이 곧 생태계 복원이 불가능한 ‘전환점’을 맞아 급격히 붕괴할 수 있다는 전망이 나와 전세계의 우려를 불러일으키고 있습니다. 6,500만년 동안 아마존 열대우림은 기후 변화에…
인간과 유인원에서 꼬리 소실 진화의 유전적 기반 Abstract 인간과 '인류형 유인원'으로 이어지는 진화 계통에서 발생한 가장 주목할만한 해부학적 변화 중 하나는 꼬리의 소실입니다. 이 변화는 인간의 이족 보행에 기여한 것으로…
합성 역방향 서열이 기본 유전체 상태를 드러낸다 Abstract 광범위한 전사 활동이 다양한 종에서 관찰됩니다. 현존하는 생물체의 게놈은 수십억 년에 걸친 진화를 겪었으며, 이러한 게놈 활동이 선택의 결과인지 아니면 '잡음'인지 분명하지…
호박벌들도 혼자서는 어려운 복잡한 행동을 다른 벌로부터 배울 수 있습니다 Abstract 문화란 사회적으로 학습되어 시간이 지남에 따라 일정하게 유지되는 행동양식을 의미합니다. 최근 연구 결과에 따르면, 동물들도 인간과 마찬가지로 선행된 혁신에…
IL-10은 sphingolipid metabolism 억하여 염증을 제한합니다. Abstract Interleukin-10(IL-10)은 innate immune cell types에서 immune cell activation과 사이토카인 생산을 제한할 수 있는 주요 anti-inflammatory cytokine입니다. IL-10 신호가 손실되면 사람과 mice에서 생명을 위협하는…
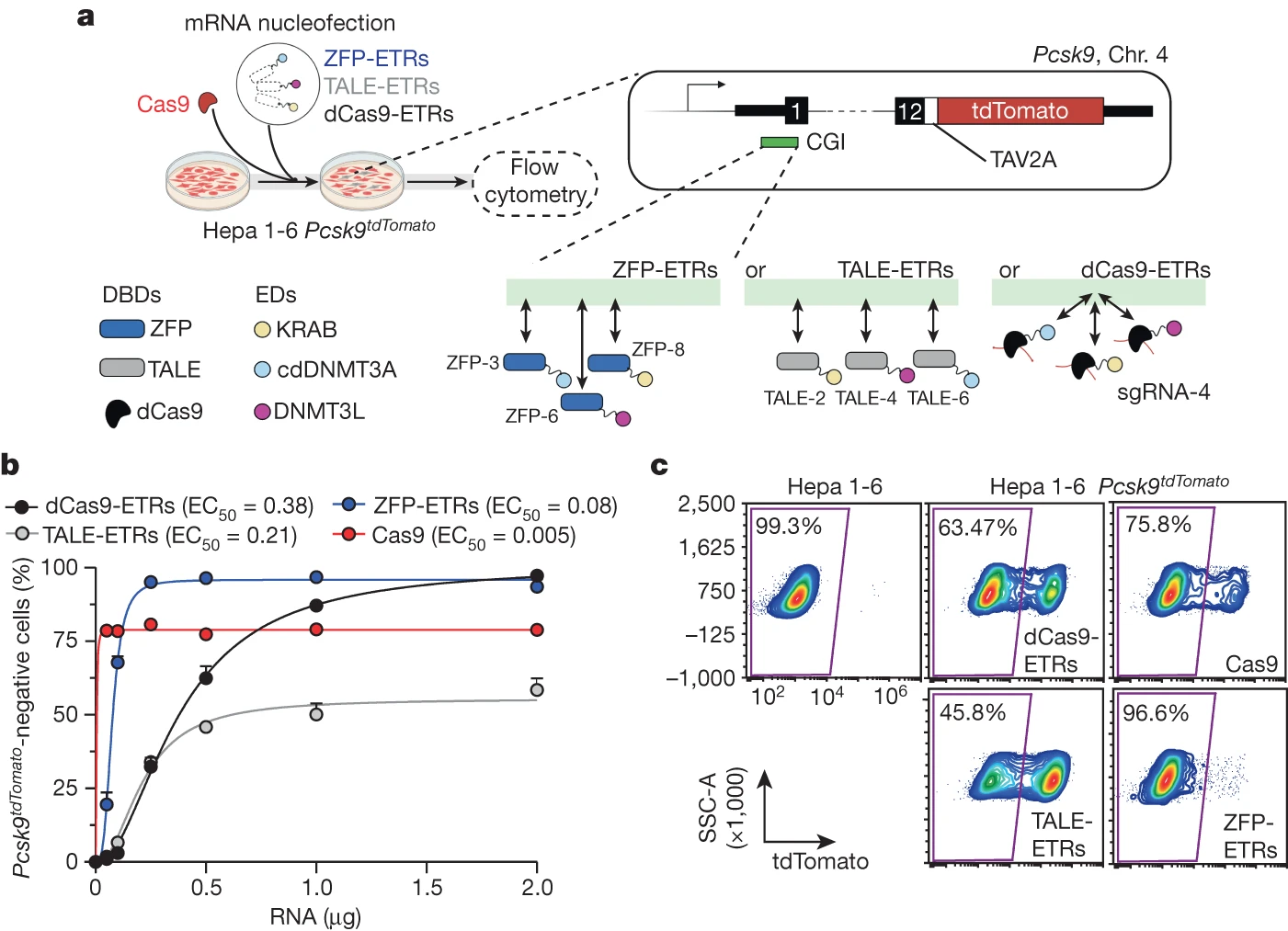
생체 내에서 지속 가능하고 효율적인 유전자 silencing을 위한 일시적 epigenome 편집 Abstract transcriptional repressors를 탑재한 programmable editors를 사용한 영구적인 epigenetic silencing은 인간 질병의 치료에 큰 가능성을 가지고 있다. 하지만, 그…
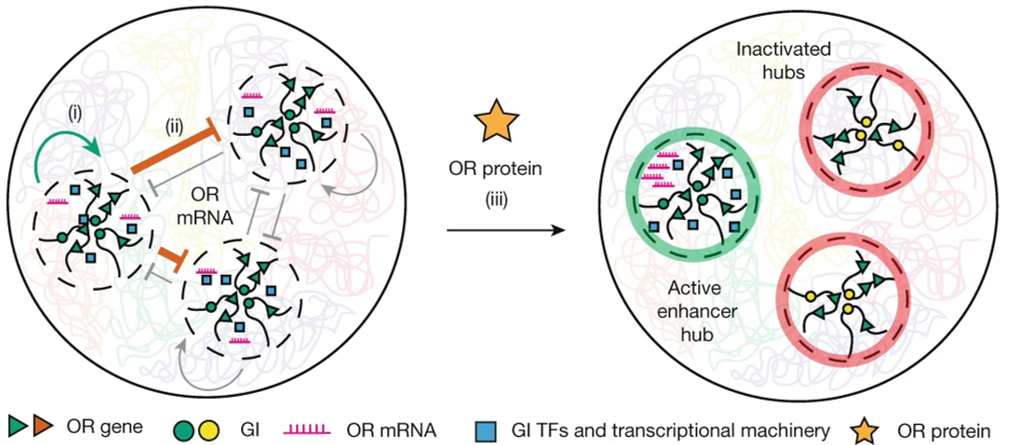
RNA 매개 symmetry breaking이 단일 후각 수용체 선택을 가능하게 한다 Abstract 후각 수용체(Olfactory Receptor, OR) 선택은 모든 후각 뉴런이 약 2,000개 이상의 OR 대립유전자 중 하나를 안정적으로 transcription하는 transcriptional dominance를…