Super-additive cooperation
초가산적 협력 Abstract 이 연구는 인간의 일회성(one-shot) 협력에 대한 진화론적 설명을 제공하려는 시도에서 출발합니다. 이 설명은 반복적인 상호작용과 집단 간 경쟁이라는 두 가지 메커니즘에 초점을 맞춥니다. 이 논문에서는 모델과 행동…
초가산적 협력 Abstract 이 연구는 인간의 일회성(one-shot) 협력에 대한 진화론적 설명을 제공하려는 시도에서 출발합니다. 이 설명은 반복적인 상호작용과 집단 간 경쟁이라는 두 가지 메커니즘에 초점을 맞춥니다. 이 논문에서는 모델과 행동…
기억 유도 운동의 기초가 되는 뇌 전반의 신경활동 Abstract 행동은 뇌 전반에 걸친 구조화된 신경 회로의 활동에 기반을 두고 있지만, 대부분의 실험은 한 번에 한 영역의 뉴런만을 탐색해왔습니다. 여러 Neuropixels…
CARD8 염증체는 HIV/SIV 병인학과 질병 진행에 지배적인 역할을 합니다. Abstract CD4+ T 세포 감소는 HIV에 감염된 사람들과 SIV-infected macaques는 SIV(Simian Immunodeficiency Virus)에 감염된 원숭이에서 질병 진행의 주요 원인이지만, 대부분의 감염되지 않은…
호박벌들도 혼자서는 어려운 복잡한 행동을 다른 벌로부터 배울 수 있습니다 Abstract 문화란 사회적으로 학습되어 시간이 지남에 따라 일정하게 유지되는 행동양식을 의미합니다. 최근 연구 결과에 따르면, 동물들도 인간과 마찬가지로 선행된 혁신에…
IL-10은 sphingolipid metabolism 억하여 염증을 제한합니다. Abstract Interleukin-10(IL-10)은 innate immune cell types에서 immune cell activation과 사이토카인 생산을 제한할 수 있는 주요 anti-inflammatory cytokine입니다. IL-10 신호가 손실되면 사람과 mice에서 생명을 위협하는…
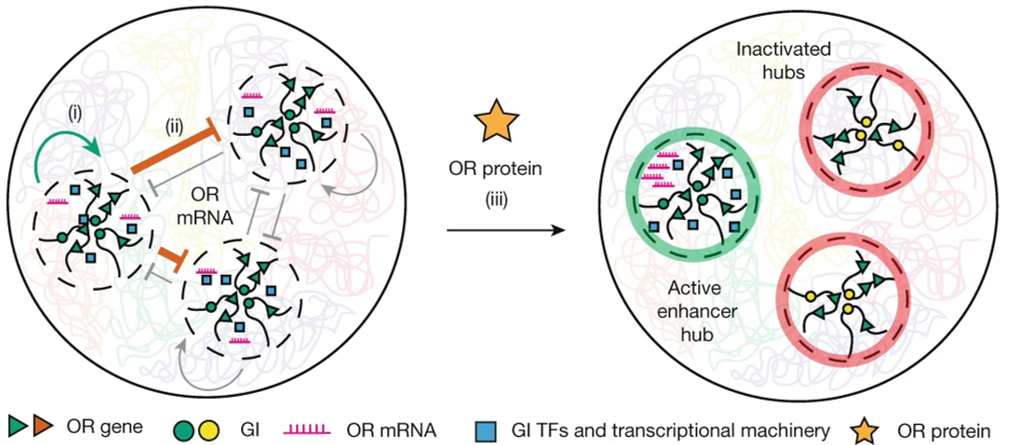
RNA 매개 symmetry breaking이 단일 후각 수용체 선택을 가능하게 한다 Abstract 후각 수용체(Olfactory Receptor, OR) 선택은 모든 후각 뉴런이 약 2,000개 이상의 OR 대립유전자 중 하나를 안정적으로 transcription하는 transcriptional dominance를…
Spatial transcriptomics을 통해 발견한 장기 기억에서 발생하는 neuron-astrocyte 간 시너지 효과 Abstract 기억은 과거의 경험을 암호화하며, 이는 미래 계획을 세우는 데 기여합니다. *Basolateral amygdala는 정서적 경험의 기초가 되는 *salience network에서…
인간 신경망 모델은 ALS(근위축성 측삭 경화증)와 FTLD(전두측두엽 변성증)에서 NPTX2 병리를 밝혀냅니다. Abstract 신경퇴행성 질환을 모델링하는 인간 세포 모델은 재현성과 지속성이 필요합니다. 이는 연령에 따라 발생하는 질병을 모사하는 데 필수적입니다. 특히,…
빛에 의해 구동되는 나노스케일의 벡터 전류 Abstract 제어된 전하 흐름은 에너지와 정보의 운반체로서, 재료의 특성과 동력학의 탐사 수단으로서, 또한 깨어진 대칭을 드러내거나 심지어 유도하는 수단으로서 과학과 기술의 많은 분야에서 근본적인…
신경퇴행에 돌연변이를 가진 E3 ligase에 의한 스트레스 반응 억제 Abstract 스트레스 반응 경로는 세포 및 조직의 안정성을 보호하기 위해 불리한 상태를 감지하고 완화시키지만, 장기간 활성화되면 세포자살과 기관의 건강을 파괴할 수…