In vivo interaction screening reveals liver-derived constraints to metastasis
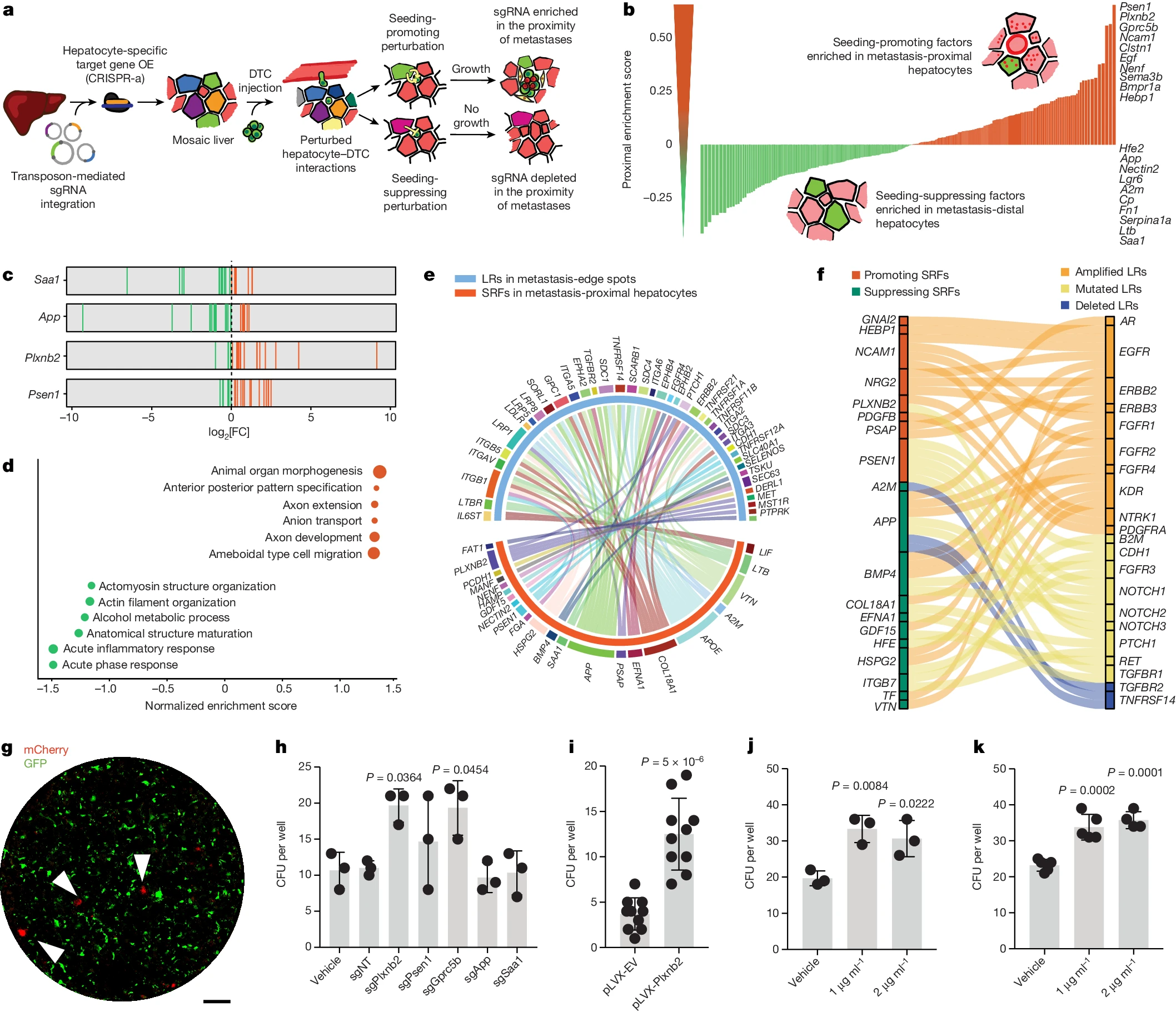
In vivo 상호작용 screening은 전이에 대한 간 유래 constraints를 밝혀낸다 Abstract 전이된 암 세포 중 단 0.02%만이 *명확한 전이(overt metastasis)를 일으킬(seed) 수 있는 것으로 추정된다. 이는 전이의 seeding에 대한 환경적…

In vivo 상호작용 screening은 전이에 대한 간 유래 constraints를 밝혀낸다 Abstract 전이된 암 세포 중 단 0.02%만이 *명확한 전이(overt metastasis)를 일으킬(seed) 수 있는 것으로 추정된다. 이는 전이의 seeding에 대한 환경적…
TERT의 clonal inactivation는 stem cell competition을 손상시킵니다. Abstract Telomerase는 chromosome ends을 보호하는 nucleoprotein caps인 telomeres를 촉매로 연장하기 때문에 줄기세포 및 암과 밀접한 관련이 있습니다. Telomerase reverse transcriptase (TERT)의 과발현은 telomere와…
인체 SARS-CoV-2 감염 모델을 통해 국소 및 전신 면역 반응 역학을 밝히다 Abstract COVID-19 팬데믹은 여전히 지속 중이며 위협적이지만, 이 질병에 대한 초기 세포 반응의 역학에 대한 이해는 제한적입니다. 이…
dsRNA 형성은 선호적인 nuclear export와 유전자 발현을 유도한다 Abstract mRNA가 핵에서 전사되고 처리된 후, 번역을 위해 세포질로 export됩니다. 이 export는 효모 Saccharomyces cerevisiae에서는 export 수용체 이합체 Mex67–Mtr2에 의해 매개되며, 인간에서는…
다중 스케일 위상학을 이용한 세포 분류: 세포내 공간 전사체학 Abstract 공간 전사체학은 조직 내 수백만 지점에서 in situ 유전자 발현을 측정합니다. 현재까지는 전사체의 깊이, 공간 해상도 및 샘플 크기 간의…
Endoplasmic reticulum–plasma membrane contact gradients가 direct cell migration을 유도합니다. Abstract Directed cell migration은 intracellular signaling의 front–back polarization에 의해 주도됩니다. Receptor tyrosine kinases 및 other inputs은 activate local signals를 활성화하여 membrane…
GLP-1과 결합한 NMDA 수용체 길항제를 통한 비만 치료 Abstract N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) 수용체는 글루타메이트에 의해 활성화되는 양이온 채널로, 뇌의 많은 생물학적 기능에서 중요한 역할을 합니다. 전장유전체연관분석(GWAS)은 글루타메이트 신경전달과 NMDA 수용체 매개…
시험관 내 소형 대장 모델을 통해 시공간적으로 해석된 대장암 발생 과정 관찰 Abstract 3차원 오가노이드 배양 기술은 종양 및 미세환경 구조를 보다 현실적이고 확장 가능하게 재현할 수 있게 하여 암…
Arabidopsis의 내열성에 필요한 온도 센서 TWA1 Abstract 과도한 온도에 노출된 식물은 생리적 도전에 대처하고 장기적인 적응을 촉진하기 위해 열 스트레스 반응을 활성화합니다. 그러나 세포 온도를 감지하여 내열성을 유도하는 메커니즘은 아직…