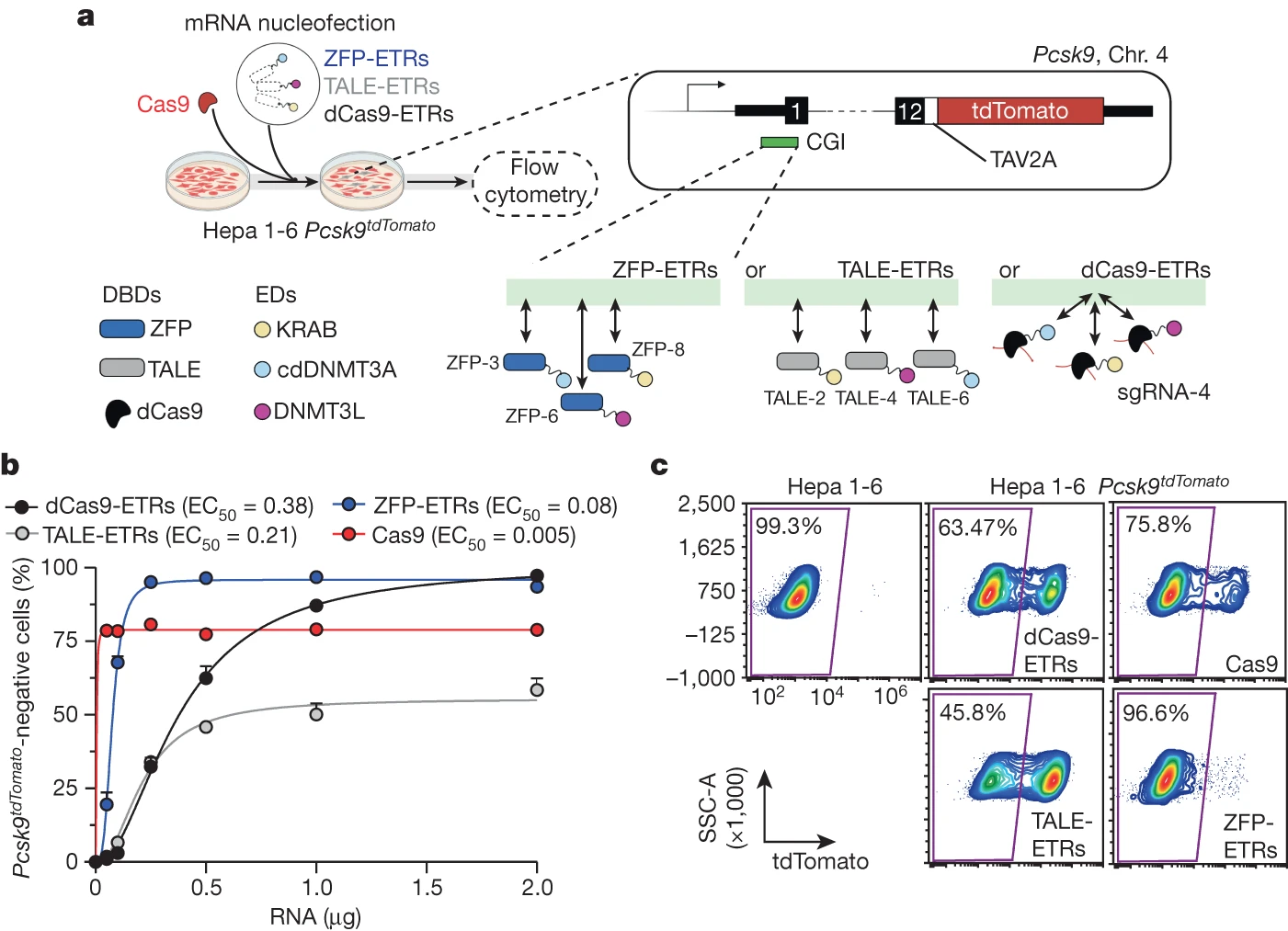
Structure of the plant plastid-encoded RNA polymerase
Structure of the plant plastid-encoded RNA polymerase Abstract 엽록체 유전자는 광합성과 관련된 단백질을 코딩하며 주로 *Plastid-encoded RNA polymerase(PEP)에 의해 전사된다. PEP은 박테리아 RNA polymerase (RNAPs)와 유사한 Plastid-encoded 단위체들로 구성된 다중-단위체…