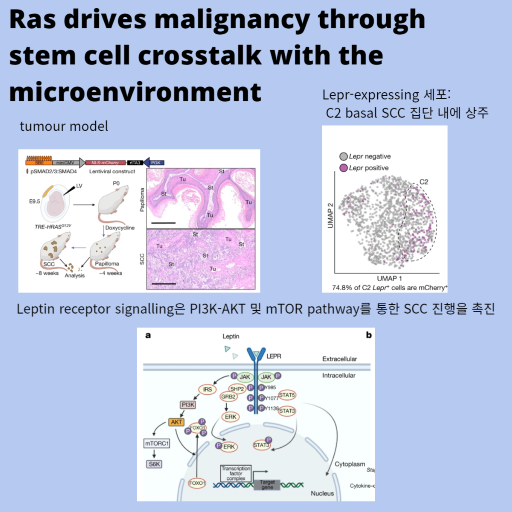
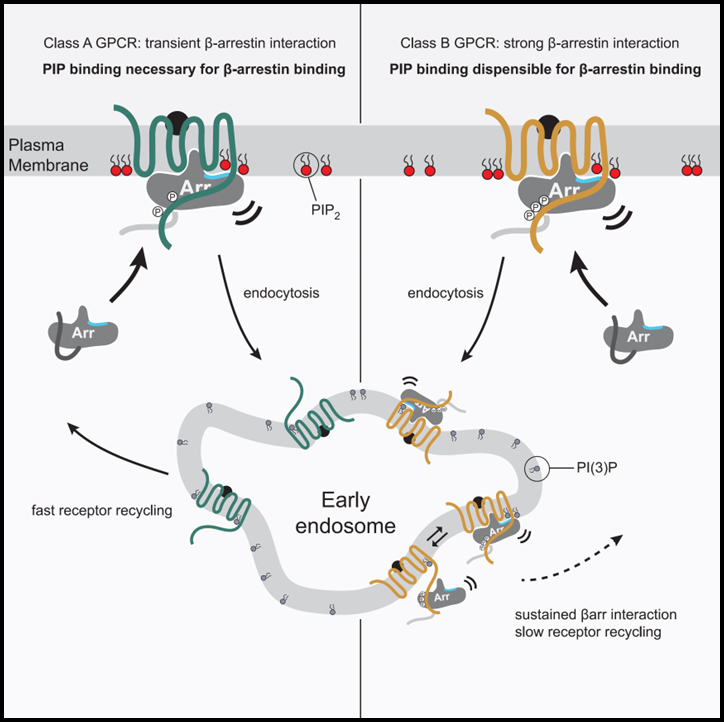
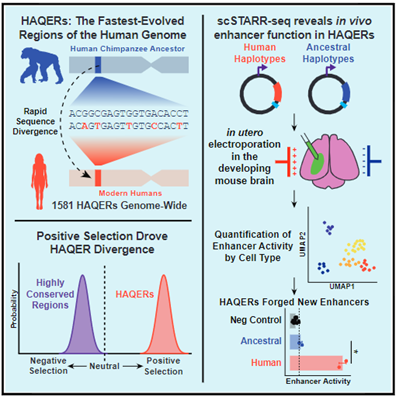
Strong cloud–circulation coupling explains weak trade cumulus feedback
강력한 cloud–circulation coupling은 약한 trade cumulus feedback을 설명한다. trade-wind(무역풍) 지역의 얕은 cumulus cloud은 태양 복사를 반사하여 지구를 식힌다. 기후 변화에 대한 trade cumulus cloud의 반응은 기후 예측의 핵심 불확실성이다. 기후…