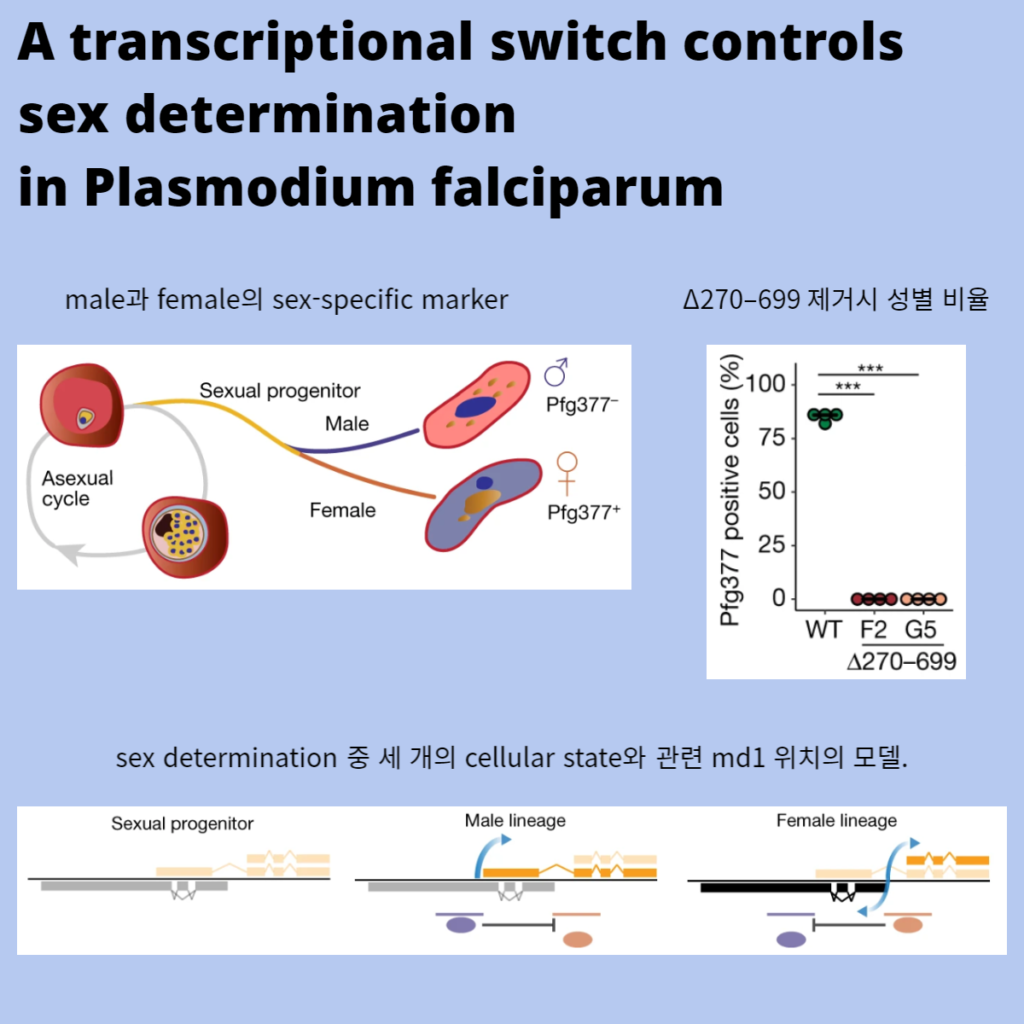
transcriptional switch는 Plasmodium falciparum에서 sex determination을 제어한다.
Abstract
Sexual reproduction과 meiotic sex는 eukaryotic tree의 생애에 깊이 뿌리를 두고 있지만, 성 또는 짝짓기 유형을 결정하는 메커니즘은 극도로 다양하며 소수의 모델 유기체에서만 잘 특징지어진다. 말라리아 기생충에서 Sexual reproduction은 벡터 숙주로의 전염과 일치한다. sex determination은 비유전적이며, 각각의 haploid 기생충은 인간 숙주에서 남성 또는 여성의 생식 세포를 생성할 수 있다. sex determination과 성 정체성 유지를 촉발하는 사건과 분자 메커니즘의 계층은 아직 설명되지 않았다. 여기서 우리는 male development 1(md1) 유전자가 인간 말라리아 기생충 Plasmodium falciparum의 남성 운명 결정에 필요하고 충분하다는 것을 보여준다. 우리는 Md1이 N 말단을 통한 sex determination과 보존된 C 말단 Lotus/OST-HTH 도메인에서 male development라는 두 가지 별개의 도메인에서 비롯된 이중 기능을 가지고 있음을 보여준다. 우리는 또한 sex determination과 결합하고 male development 유전자가 female lineage에서 발현되지 않도록 하는 md1 위치에서 bistable switch를 식별한다. 우리는 진핵생물에서 sex determination의 몇 가지 알려진 비유전적 메커니즘 중 하나를 설명하고 말라리아 전염을 차단하는 개입의 잠재적 대상으로 Md1을 강조한다.
Figure
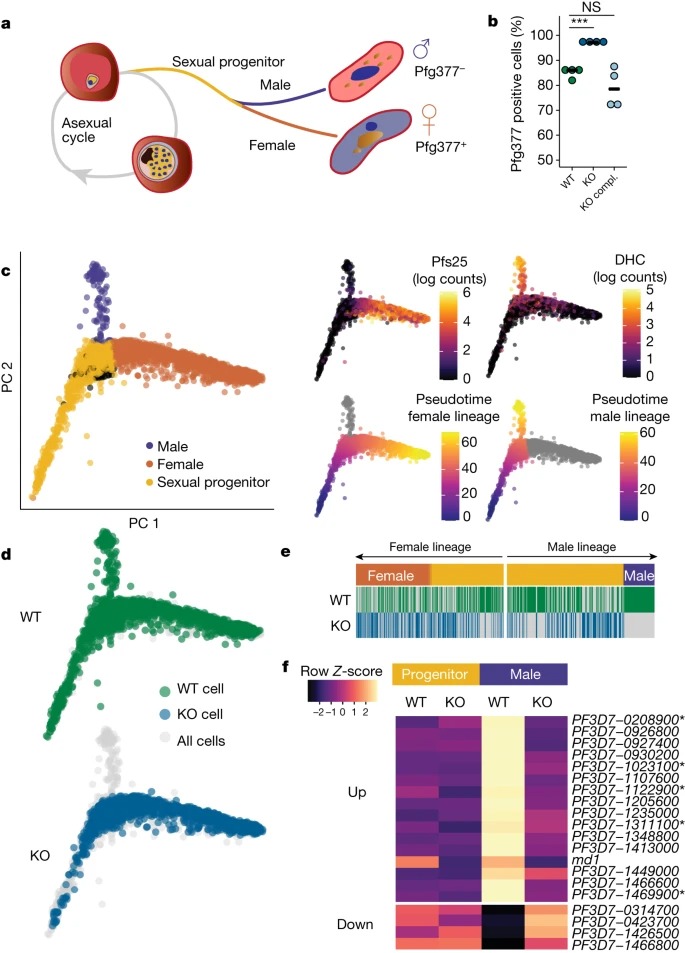
Fig. 1: md1은 male fate를 결정하는데 필요하다.
a, Asexually replicating parasite는 sexual development로 bifurcate될 수 있으며, 처음에는 sexual progenitor state로 특징지어지며, 이후에 남성 또는 여성으로 분화된다.
b, WT, KO and a complemented KO (KO compl.)에서 immunofluorescence에 의한 Pfg377-positive gametocyte의 비율(4개의 생물학적 복제).
c, female (Pfs25)과 male (DHC, PF3D7_0905300)의 sex-specific marker에 의해 확인된 바와 같이 male and female branch로 sexual progenitor cell의 분기를 다루는 single-cell transcriptome의 Combined principal component (PC) analysis.
d, 하이라이트된 WT and KO cell.
e, 각 pseudotime path를 따라 유전자형을 나타내며, 각 세포는 녹색(WT) 또는 파란색(KO) 막대가 발달 경로를 따라 배치된다.
f, male developmental path의 첫 번째 유전자를 확인하기 위해 male sex-determining event의 양쪽에 있는 50개의 세포를 사용하여 differential expression analysis을 수행.
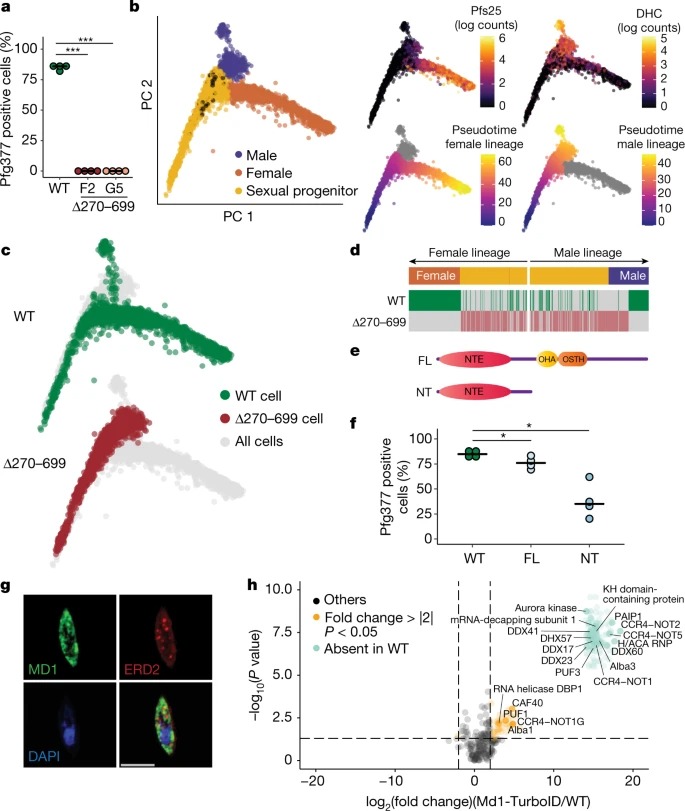
Fig. 2: md1은 male fate를 결정하기에 충분하다.
a, WT와 두 개의 클론에서 IFA에 의한 Pfg377-positive gametocyte (female-specific)의 비율
b, female (Pfs25)과 male (DHC, PF3D7_0905300) sex-specific marker로 식별된 male and female branch로 progenitor cell의 분기를 다루는 single-cell transcriptome의 Combined principal component analysis.
c, 하이라이트된 WT and Δ270–699 cell.
d, 각 developmental pseudotime 순서에 따른 두 유전자형의 표현.
e, episome에서 translated된 Md1 단백질 버전의 도식.
f, 과발현 라인에서 Pfg377-positive gametocyte의 비율(생물학적 복제 4개).
g, Md1이 cytoplasmic foci에 존재하고 the nucleus에는 존재하지 않음을 보여주는 Md1-3xHA gametocyte의 IFA.
h, MS of Md1-TurboID versus WT (untagged)의 proximity labelling을 확인된 단백질의 volcano plot.
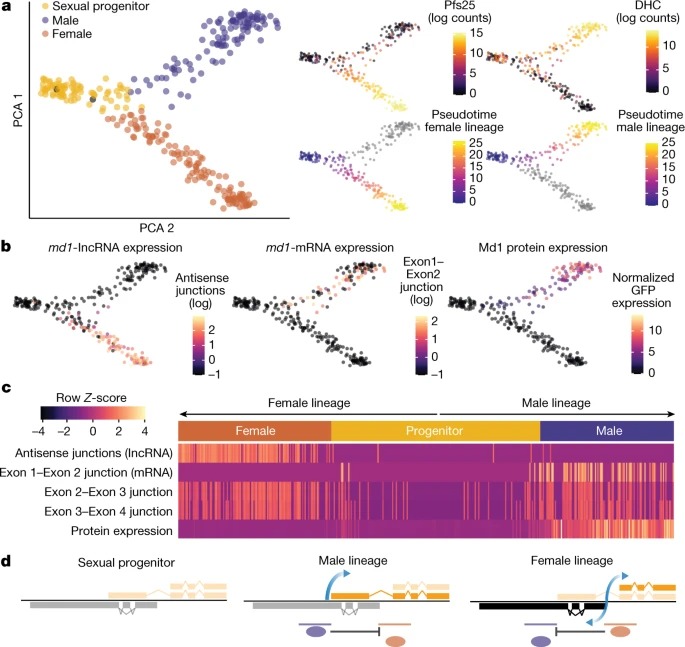
Fig. 3: md1 locus에서의 transcriptional and translational pattern은 sex-determining event 와 관련이 있다.
a, female (Pfs25)과 male (DHC, PF3D7_0905300) sex-specific marker로 식별된 male and female branch로 progenitor cell의 분기를 다루는 single-cell transcriptome의 Principal component analysis.
b,c, sex-determining event (b) 동안 exon–exon junction 수와 normalized GFP 강도(Md1 단백질) 에 의해 측정되고, 각 developmental pseudotime 순서(c)를 따라 표시되는 다양한 md1 transcript의 발현.
d, sex determination 중 세 개의 cellular state와 관련 md1 위치의 모델.
Disscussion
Sexual commitment와 sex determination은 겉보기에 세포 운명의 결정이다. Sexual commitment는 이전 asexual cycle에서 발생하고 exclusively sexual progeny를 낳거나 같은 사이클 내에 발생하는 것으로 생각된다. 초기 연구에서는 single committed schizont가 대부분 남성 또는 여성 자손을 낳을 것이라고 제안했으며, 이전 asexual cycle에서 sex determination을 시사했으며, 이러한 연구 중 하나는 혼합 자손을 관찰했다는 경고이다. 그러나 이러한 연구는 결정 포인트가 탐구되지 않은 same-cycle commitment의 발견에 선행한다. 남성도 여성도 아니고 결정보다 앞서는 transcriptional sexual progenitor state가 존재한다는 우리의 관찰은 transcriptional sex determination의 시기를 평가하도록 자극했다. bulk timecourse와의 상관관계는 stage II and III 사이에 생식세포가 transcriptionally dimorphic 된다는 것을 시사한다(Extended Data Fig. 6g). 또한, 우리는 sex determination event (Fig. 3c)과 결합된 Md1-2A-GFP 단백질 발현이 gametocytogenesis 4일차(Extended Data Fig. 6h) 전후에 처음 나타나고, GFP-positive cell은 stage III 이상(Extended Data Fig. 6i)이라는 것을 발견했다. 비록 우리는 transcriptionally silent sex-determined state가 있을 가능성을 무시하지 않지만, 우리의 데이터는 성 결정이 stage II to III 로 전환하는 동안 gametocytogenesis의 4일차 즈음에 일어난다는 것을 강력하게 시사한다.
요약하면, 우리는 말라리아 기생충에서 Md1을 sex-determining effector로 식별했다. 흥미롭게도, 우리는 단백질의 N 말단만이 남성의 운명을 특정하는데 필요하다는 것을 발견했다. 단백질의 이 부분은 hematozoa 밖에서 보존되지 않으며(확장 데이터 그림 2a), sex-determining gene이 일반적으로 빠르게 진화한다는 개념과 일치한다. 대조적으로, Md1 C 말단은 sex determination에 필요하지만 male gametocyte에서 developmental effector로서 중요한 OST-HT/LOTUS 도메인을 포함한다. 두 기능이 동일한 분자 경로를 통해 발휘되는지, 또는 이 도메인 융합이 남성 운명의 특정 이후 적절한 maturation을 보장하기 위한 안전 잠금 메커니즘인지는 알려지지 않았다. Md1은 cytoplasmic granule에 국소화되고 RNP granule protein과 상호작용하여 eukaryotic tree의 생애의 발달 과정의 허브로서 LOTUS-containing protein을 더욱 강조한다. 마지막으로, md1 위치의 복잡한 유전자 조절 패턴은 sex determination의 centrality에 대한 추가 증거를 제공한다. 유전적으로 결정된 시스템에서 세포 운명 조절은 성별을 결정하는 위치의 유무에 의존할 수 있다. 우리는 유전적으로 동일한 세포에서 sex determination이 세포의 성적 운명의 조절기 주변의 강력한 규제 아키텍처를 필요로 한다는 것을 보여준다.