lateral plate mesoderm에서 유래한 median fin와 paired fins의 기원.
Abstract
쌍을 이루는 appendages의 발달은 진화 과정에서 핵심적인 혁신이었으며 척추동물의 수중에서 육지로의 전환을 촉진했습니다. paired fins의 진화에 대한 한 가설은 주로 lateral plate mesoderm (LPM)에서 유래한 것으로, pectoral and pelvic fin territories 사이에 위치한 lateral fin folds를 통해 unpaired median fins에서 파생되었다는 것입니다. unpaired and paired fins는 구조적, 분자적 특성이 비슷하지만, 현존하거나 멸종한 종의 유충이나 성체에서 paired lateral fin folds에 대한 확실한 증거는 존재하지 않습니다. 쌍을 이루지 않는 unpaired fin core components는 paraxial mesoderm에서 독점적으로 파생된 것으로 간주되기 때문에 모든 전환은 fin developmental programme이 LPM에 대한 co-option과 bilateral duplication을 모두 가정합니다.
여기서 우리는 larval zebrafish unpaired pre-anal fin fold (PAFF)이 LPM에서 median and paired fins의 developmental intermediate를 나타낼 수 있음을 확인했습니다. 우리는 cyclostomes and gnathostomes 모두에서 PAFF에 대한 LPM의 기여를 추적하여 이것이 척추 동물의 고대 특성이라는 개념을 뒷받침합니다. 마지막으로, 우리는 bone morphogenetic protein signalling을 증가시킴으로써 PAFF가 분기되어 LPM-derived paired fin folds을 생성할 수 있음을 관찰했습니다. 우리의 연구는 ateral fin folds가 paired fins로의 정교화를위한 embryonic anlage로 존재했을 수 있다는 증거를 제공합니다.
Figure
Fig. 1: A non-PM-derived median fin fold.
a, Larval 4 dpf zebrafish는 caudal median fin fold (청록색 화살촉) 외에 median PAFF(노란색 화살촉)를 가지고 있습니다.
b, 3 dpf Tg(tbx16l:GAL4-VP16)의 Confocal image.
c-e, ET37 Enhancer Trap transgenic line의 pre-anal (c), ventral caudal (d) and pectoral (e) fins의 Confocal images로 PAFF가 다른 larval fin folds과 형태학적으로 유사한 mesenchyme (화살촉으로 표시)을 포함하고 있음을 나타냅니다.
f, 3dpf에서 PAFF(노란색 화살촉)와 caudal fin fold (청록색 화살촉) 모두에서 fin mesenchyme marker fbln1의 in situ hybridization.
g,h, 5 dpf Tg(-5.2lyve1b:DsRed) transgenic line의 pre-anal (g) and caudal (h) fin folds의 mesenchyme에서 DsRed 발현.
i,j, 8개의 dpf frf mutants에서 collagen II에 대한 Immunostaining (j)은 WT(i)와 비교하여 fibril organization이 손실되었음을 보여줍니다.
Fig. 2: The PAFF is an LPM-derived median fin fold.
a,b, caudal fin fold (청록색 윤곽선)이 아닌 mesenchyme of the pectoral (초록 윤곽선 및 화살촉, 삽입부에서 확대됨)과 PAFF(노랑 윤곽선 및 화살촉)의 eGFP 라벨링을 보여주는 2dpf(a) 및 3dpf(b)에서의 Tg(hand2:EGFP) embryos의 Confocal images.
c,d, 3dpf에서 hand2의 In situ hybridization는 PAFF에서만 hand2의 fin expression을 보여줍니다 (c). Nomarski optics으로 더 높은 배율은 mesenchyme에서의 발현을 나타냅니다 (d).
e, LPM lineage tracing transgenes의 개략도.
f, imaging 전 4-OHT treatment 및 heat shock 후 (e)에 표시된 transgenics을 사용한 LPM의 Lineage tracing은 PAFF mesenchyme이 LPM에서 유래되었음을 보여줍니다(노란색 화살촉 및 삽입에서 확대).
g,h, (g)에 윤곽이 표시된 LPM 영역에서 ultra-violet laser photoconversion 후 10-somite stage (10초)(g) 및 48시간(hpf)에서 drl:H2B-Dendra2 transgenic line의 Ventral (g) 및 lateral (h) confocal images.
Fig. 3: hand2의 PAFF mesenchyme expression은 vertebrates 전반에 걸쳐 보존되어 있습니다.
a,b, mesenchymal cells (노란색 화살촉)이 dispersed된 PAFF(a)를 보여주는 9개의 dpf medaka의 Nomarski images (b).
c, pre-anal fin mesenchyme (노란색 화살촉)에서 hand2 발현을 보여주는 39단계 medaka의 In situ hybridization.
d,e, 36 paddlefish embryos에서 hand2의 In situ hybridization를 laterally (d) 또는 transverse section (e)으로 표시한 모습.
f,g, E29 단계 lamprey (P. 마리 누스) embryos의 HandA in situ hybridization를 laterally (f) 또는 transverse section (g)으로 보여줍니다.
h-j, 42단계 X에서 hand2의 Chromogenic (h) 또는 fluorescent (i,j) in situ hybridization.
Fig. 4: PAFF를 paired fin folds로 복제합니다.
a,b, MO targeting chordin를 주입한 5 dpf(a) 및 4 dpf(b) embryos의 PAFF의 Lateral (a) 및 ventral (b) Nomarski images로, PAFF가 중복되어 있습니다(노란색 화살촉).
c,d, ventrally 이미지화 된 4 dpf ET37 transgenic larvae에서 PAFF를 주입하지 않거나 (c) chrd MO를 주입 한 (d) Confocal micrographs.
e, 위에 표시된 transgenic line의 chrd MO 복제 PAFF의 Ventral confocal image.
f–i, 8dpf(f) 및 6dpf(g-i)에서의 Tg(hand2:EGFP) larvae의 Light-sheet (f) 및 confocal (g-i) images.
j,k, 6 dpf에서 Ranchu goldfish PAFF의 Lateral low- (j) 및 high-power (k) Nomarski images
l-n, hand2에 대한 in situ hybridization로 염색한 7 dpf Ranchu larvae의 pre-anal (l,n) 및 caudal fin folds (m)의 Lateral (l,m) 및 transverse (n) 보기, 여기서 hand2 양성 PAFF 중간엽은 노란색 화살촉으로 표시되어 있습니다.

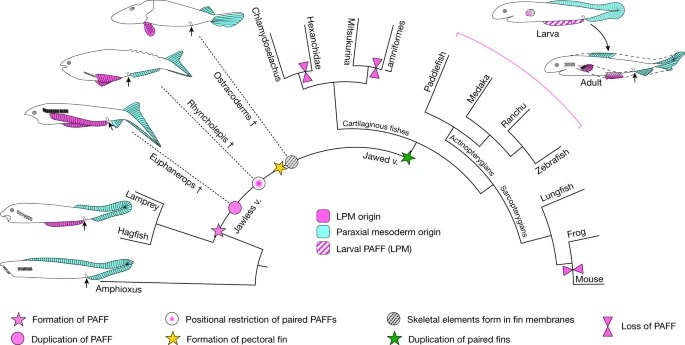
Fig. 5: paired fins에 대한 PAFF의 elaboration에 대한 가설.
vertebrates의 단순화 된 진화 시나리오는 PAFF의 존재와 paired fins로 이어지는 subsequent modifications을 보여줍니다.
Disscussion
우리의 연구는 larval median fin programme을 LPM에 적용하고 fin duplication과 pectoral and pelvic fins로의 regionalization을 통해 paired fin evolution에 대한 모델에 무게를 실어줍니다. 우리는 PAFF가 어떻게 LPM-derived paired fins를 생성하게 되었는지에 대한 한 가지 가능한 모델을 제시합니다(FIg 5). PAFF는 small ectoderm-only fin fold로 시작되었을 수 있습니다. persistence of a somatopleure and/or a lateral mesodermal divide와 같은 LPM topology의 변경에 따라 LPM 기여도가 이후에 진화할 수 있습니다. 유사한 LPM 조직 맥락이 PAFF의 elongation과 duplication에 따른 paired fin regionalization로 이어졌을 수 있습니다. PAFF는 unpaired and paired fins의 특징을 모두 가지고 있기 때문에 새로운 진화 모듈을 나타내거나 적어도 paired appendages의 출현에 기여한 발달 메커니즘의 구성 요소를 보여줄 수 있습니다.